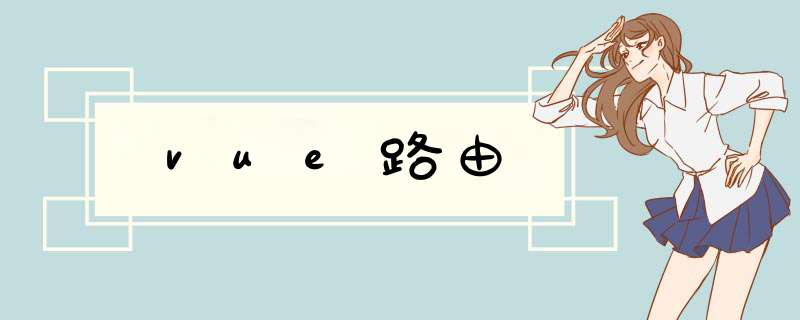
<router-link to="需要跳转到页面的路径">
1、this.$router.push()跳转到指定的url,并在history中添加记录,点击回退返回到上一个页面
2、this.$router.replace()跳转到指定的url,但是history中不会添加记录,点击回退到上上个页面
3、this.$touter.go(n)向前或者后跳转n个页面,n可以是正数也可以是负数
前端路由(单页应用程序): 一个url地址,对应哪个组件
1.背景知识
hash值hash是url的一部分
hash的变化 不会引起页面刷新
hash可以通过window.onhashchange监听到
2.实现原理
监听onhashchange的变化
写配置规则: hash是xxx的时,去加载什么组件
后端路由:一个接口地址,对应哪一段接口地址
目标 : 页面不刷新,地址栏变化,页面内容变化。
Router-link组件介绍
作用: 用于提供路由链接,实现页面跳转
格式:
要点:
**
1.是vue-router提供的组件
2. router-link最终会渲染成a链接
3.router-link自带链接导航高亮的功能**
<template>
<div>
<h1>App组件</h1>
<ul>
<li><router-link to="/home">首页</router-link></li>
<li><router-link to="/movie">电影</router-link></li>
<li><router-link to="/about">关于</router-link></li>
</ul>
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</template>
router-link-exact-active router-link-active
小结
链接导航, 用router-link配合to, 实现点击切换路由
1.router-link组件会被vue解析成a标签,但不能直接通过a标签来跳转。
2 如果当前路由被激活会添加特殊的类名:
url?key=val&key=val
vue路由传参的方式
两种方式:
1. query传参。 适用场景:页面搜索
2. params传参。 适用场景:详情页
接收路上由上传递的参数和值
<div>
你要浏览的商品是: {{ $route.query.name }} {{ $route.params.goodsId}}
</div>
路由定义
{
path: "/goods",
component: MyGoods
},
{
path: "/goods/:goodsId",
component: MyGoods
},
页面跳转传值
<li><router-link to="/goods?name=外套">外套</router-link></li>
<li><router-link to="/goods/123">详情</router-link></li>
params
?key=value =》 用
r
o
u
t
e
.
q
u
e
r
y
.
k
e
y
取
值
/
值
−
需
要
提
前
在
路
由
规
则
/
p
a
t
h
/
:
k
e
y
=
》
用
route.query.key 取值 /值-需要提前在路由规则/path/:key =》 用
route.query.key取值/值−需要提前在路由规则/path/:key=》用route.params.key 取值
重定向, 用户访问的是A地址,系统把它切换到B地址。
应用场景:改变默认访问页面的行为
const routes = [
{
path: "/",
redirect: "/home" // 重定向
}
]
路由404 统一处理异常地址:那些个正常配置的地址之外的地址。
import NotFound from "@/components/NotFound";
const routes = [
{
path: "/",
redirect: "/home" // 重定向
},
// ...正常路由
{ // 当上面路由都不匹配, 匹配这个通配符, 显示NotFound页面
path: "*",
component: NotFound
}
]
编程式: 写代码
导航:页面跳转 编程式导航 ====> 写代码的方式来让页面跳转
// 跳转页面不传参
this.$router.push('/路由路径')
this.$router.push({path: '路由路径'})
this.$router.push({name: '路由名称'})
// 跳转并query传参-方式1
this.$router.push("/路由路径?参数1=值1&参数2=值2")
// 跳转并query传参-方式2
this.$router.push({
path: "路由路径",
query: {
"参数1":值1,
"参数2":值2
}
})
// 跳转并params传参-方式1
this.$router.push("/路由路径/值1/值2")
// 跳转并params传参-方式2
this.$router.push({
name: "路由名称",
params: {
"参数1":值1,
"参数2":值2
}
})
// 后退
$router.back()
原理:router-view中再次包含router-view。
背景:一个组件内部包含的业务还是很复杂,需要再次进行拆分。
routes:[
{
path: '/page1',
component: Page1, // 这个组件内部还有router-view
children: [
{
path:'', // path为空,表示当 #/page1时,显示 Page1组件+组件1
component: 组件1 //
},
{
path:'/xx1', // path以/开头,表示当 #/xx1时,显示 Page1组件+组件2
component: 组件2
},
{
path:'xx2', // path以/开头,表示当 /page1/xx2时,显示 Page1组件+组件3
component: 组件3
}
]
}
]
1. 在已有的路由容器中,再实现一套路由,再套一个路由容器,叫:嵌套路由。
2. 嵌套路由除了 router-view 之间需要嵌套,路由规则也需要通过children来实现嵌套。
创建路由文件router/index.js
// 导入路由插件
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import Vue from 'vue'
// 使用插件 - 重要
Vue.use(VueRouter)
// 导入组件
import Page1 from './Page1.vue'
import Page2 from './Page2.vue'
import Page3 from './Page3.vue'
// 创建路由规则
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{
path: "/page1", // 当浏览器访问 http://localhost:8080/#/page1时,
component: Page1 // 装入组件 Page1
},
{
path: "/page2",
component: Page2
},
{
path: "/page3",
component: Page3
}
]
})
export default router
使用路由 在main.js中
import router from './router/index.js'
new Vue({
router: router, // 使用路由
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')
使用路由
<router-view></router-view>
测试: 在地址栏中输入地址来访问
使用router-view挂载点显示切换的路由
vue-router使用步骤创建新项目,可以自定义安装配置vue-router(不用自己写任何代码)
老项目+手动引入vue-router
!请添加图片描述
目标: 路由跳转之前, 会触发一个函数
语法
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {})
案例: 在跳转路由前, 判断用户登陆了才能去<我的音乐>页面, 未登录d窗提示回到发现音乐页面
在router/index.js 路由对象上使用固定方法beforeEach
// 路由前置守卫
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
// to代表要跳转到哪个路径去, to的值是个对象可以打印看到
// from代表从哪个路径跳过去
console.log(to);
console.log(from);
// fullPath带?后面参数的, path是完整的路径
console.log("路由要跳转了");
// 模拟判断登录了没有, 登录后才能去我的音乐
let loginFlag = false; // 假设false代表未登录
if (to.path == "/my" && loginFlag == false) {
// 如果去个人中心页面, 判断未登录, 提示登录(并强制跳转回find)
alert("请先登录!");
next("/find");
} else {
// 如果不去/my页面就直接跳转
next();
}
});
目标: 路由跳转后, 触发的函数
语法:router.afterEach((to, from) => {})
使用:router/index.js - 添加
router.afterEach((to, form) => {
console.log(to);
console.log(form);
console.log("路由发生了跳转");
})
添加链接描述
目标: 修改路由在地址栏的模式
router/index.js
const router = new VueRouter({
routes,
mode: "history" // 打包上线后需要后台支持
})
**history和hash模式对比:
功能一样(跳转页面)history模式的path路径不带#号,hash有#号hash模式兼容性好**history和hash模式对比:
它们都实现页面的跳转功能一样(跳转页面)它们的区别体现在3个方面a. 外观:history模式的path路径不带#号,hash有#号
b. 原理:hash模式使用onhashchange , history使用pushState。导致有兼容性的差异。hash模式兼容性好(对浏览器的兼容性,onhashchange ),history的兼容性比hash模式差一些 (底层使用的API是Html5的API: ,对浏览器有一定的要求。 )
c. 项目上线之后有区别。history开发的项目,在打包上线之后,需要后端配置来支持,不然就会出现404页面。官网上有介绍。我在开发中,没有特殊的要求,一般就用hash。如果要修改模式,就改mode: “history”为啥会有404页面?
a. history访问这个地址时, http://www.xxx.com/find ,后端收到的 req.url 是 /find, 但是我们是单页应用程序,我们只有一个资源是index.html,没有资源叫/find,所有就会报404。
b. history访问这个地址时, http://www.xxx.com/#/find ,后端收到的 req.url 是 /, 有一个资源是index.html,能正常显示
hash路由例如:
history路由例如:
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)