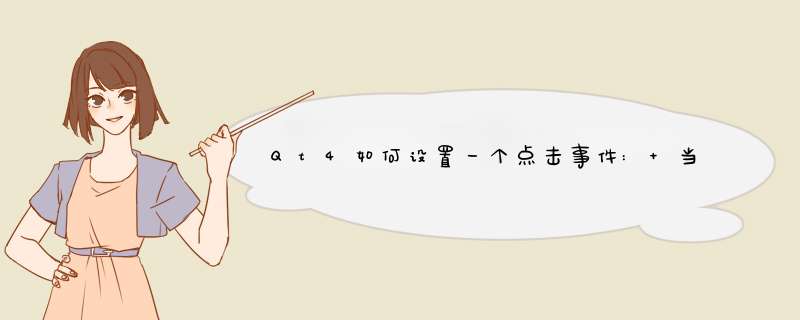
void MainWidget::startProcess()
{
//启动process
}
QT中使用QProcess启用外部程序启用外部程序,并可传参,默认第一个参数是exe路径!启动外部程序的方法有以下两种:1、start()void QProcess::start ( const QString &program, const QStringList &arguments, OpenMode mode = ReadWrite )Starts the program program in a new process, passing the command line arguments in arguments. The OpenMode is set to mode. QProcess will immediately enter the Starting state. If the process starts successfully,QProcess will emit started()otherwise, error() will be emitted.Note that arguments that contain spaces are not passed to the process as separate arguments.Windows: Arguments that contain spaces are wrapped in quotes.Note: Processes are started asynchronously, which means the started() and error() signals may be delayed. Call waitForStarted() to make sure the process has started (or has failed to start) and those signals have been emitted.See also pid(), started(), and waitForStarted().2、使用QProcess::execute(), 不过使用此方法时程序会最阻塞直到此方法执行的程序结束后返回,这时候可使用QProcess和QThread这两个类结合使用的方法来处理,以防止在主 线程中调用而导致阻塞的情况先从QThread继承一个类,重新实现run()函数:答:1、使用QProcess::startDetached()方法,启动外部程序后立即返回;2、使用QProcess::execute(),不过使用此方法时程序会最阻塞直到此方法执行的程序结束后返回,这时候可使用QProcess和QThread这两个类结合使用的方法来处理,以防止在主线程中调用而导致阻塞的情况先从QThread继承一个类,重新实现run()函数:Quote:class MyThread : public QThread{public:void run()}void MyThread::run(){QProcess::execute("notepad.exe")你这个需求可以使用popen()来实现。FILE * file = popen("/linphonec", "w")
...
fwrite("call xxxx\r\n", 11, file)
fwrite("terminate\r\n", 11, file)
...
pclose(file)
你可以在QT的按钮slot里向file写入命令,这些命令就能传到linphone的stdin。
这么做的不足 1. popen只能打开单向管道 因此你读不到linphone的输出结果。2. popen在较低版本的uclibc上不是thread safe的
变通的办法是你改一下linphone,调用freopen来重定向自己的stdin和stdout
不过我觉得你最好还是改改linphone,集成到你的QT程序里算了,也不麻烦
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)