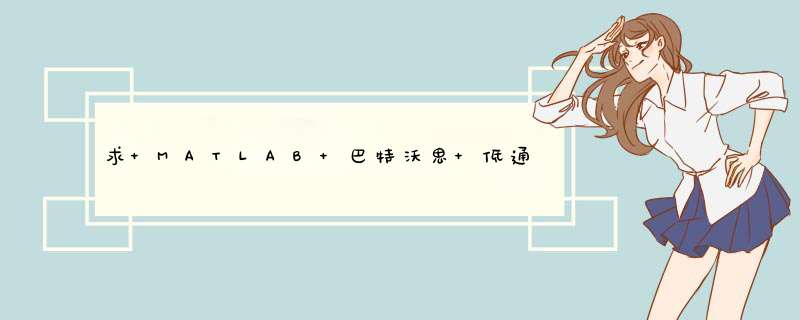
[bz,az]=impinvar(b,a,Fs)
[bz,az]=impinvar(b,a)
例如:取采样频率f=1KHz,用双线性变换法设计五阶Butterworth低通数字滤波器,绘出模拟滤波器与数字滤波器的幅频与相频特性,MATLAB程序如下:
[z,p,k]=buttap(5) % 设计五阶Butterworth低通模拟滤波器原型
[zd,pd,kd]=bilinear(z,p,k,1000)%双线性变换得到低通数字滤波器
[b,a]=zp2tf(zd,pd,kd)%滤波器类型转换
w=128
freqs(b,a,w)
figure
freqz(b,a,w)
实例:1、设带通滤波镇拆器的滤波器中心频率为W0=2KHz,带宽为BW=100Hz, 取采样频率f=10kHZ,用脉冲相应不变法设计,设计五阶带通Butterworth数字滤波器,绘出数字滤波器的频谱特性
[z,p,k]=buttap(5)
[b,a]=zp2tf(z,p,k)
w=128
w0=2000
[bt,at]=lp2bp(b,a,w0,10000)
[bz,az]=impinvar(b,a,w)
freqz(bt,at,w)
2、直接设计五阶butterworth带通滤波器,绘出频谱图。(高端与低端截止频率分别为0.2和0.9)
figure
w=[0.2,0.9]
[b,a]=butter(5,w)
freqz(b,a)
3、设高通截止频率为w0=10000Hz, 取采样频率f=20000,用指正双线性变换法设计六阶高通Butterworth数字滤波器,绘出数字滤波器的频谱特性
[z,p,k]=besselap(6)
[b,a]=zp2tf(z,p,k)
w=128
w0=10000
[bt,at]=lp2hp(b,a,w0)
[bz,az]=bilinear(bt,at,20000)
freqz(bz,az,w)
4、取采样频率f=100Hz,用双线性变换法设计五阶Butterworth低通数字滤波器,绘出模拟滤波器与数字滤波器的幅频与相频特性
御逗枣 [z,p,k]=buttap(5)
[zd,pd,kd]=bilinear(z,p,k,100)
[b,a]=zp2tf(zd,pd,kd)
w=128
freqs(b,a,w)
figure
freqz(b,a,w)
具体的得根据情况自己确定
/// 巴特沃斯滤波器, 带增益Mat BoostButterworthFilter( const int &row, const int &col, const float &cutoff, const int &n, const float &boost )const
{
assert( row>1 && col>1 )
assert( cutoff>0 && cutoff<0.5 )
assert( n>=1 )
if ( boost>=1 )
{
return (1-1/boost)*( BHPF( row, col, cutoff, n ) ) + 1/boost
}
else
{
return (1-boost)*BLPF( row, col, cutoff, n) + boost
迅梁}
}
/// 巴特沃斯高通滤波器
Mat CIllumNorm::BHPF( const int &row, const int &col, const float &cutoff, const int &n )
{
return 1-BLPF( row, col, cutoff, n )
}
/// 巴特沃斯低通滤波器
/*
cutoff is the cutoff frequency of the filter 0 - 0.5
n is the order of the filter, the higher n is the sharper
1
f = --------------------
升镇 2n
1.0 + (w/cutoff)
*/
Mat BLPF( const int &row, const int &col, const float &cutoff, const int &n )
{
assert( row>1 && col>1 )
assert( cutoff>0 && cutoff<0.5 )
assert( n>=1 )
Mat X = Mat::zeros( row, col, CV_32F )
Mat Y = Mat::zeros( row, col, CV_32F )
if ( col%2 )
{
int t = -(col-1)/2
for ( int j=0 j<col j++ )
{
for ( int i=0 i<row i++ )
{
X.at<float>( i, j ) = ((float)t)/(col-1)
}
t++
}
}
else
{
int t = -col/2
for ( int j=0 j<col j++ )
{
for ( int i=0 i<row i++ )
{
X.at<float>( i, j ) = ((float)t)/col
}
t++
}
}
if ( row%2 )
{
int t = -(row-1)/2
for ( int i=0 i<row i++ )
{
for ( int j=0 j<col j++ )
{
Y.at<float>( i, j ) = ((float)t)/(row-1)
}
t++
}
}
else
{
int t = -row/2
for ( int i=0 i<row i++ )
{
for ( int j=0 j<col j++ )
{
Y.at<float>( i, j ) = ((float)t)/row
}
t++
}
}
Mat H = Mat::zeros( row, col, CV_32F )
/// 计算频域的巴特沃斯分类器
for ( int i=0 i<row i++ )
{
for ( int j=0 j<col j++ )
{
float x = X.at<float>( i, j )
float y = Y.at<float>( i, j )
float radius = sqrtf( x*x + y*y )
/// 1.0 ./ (1.0 + (radius ./ cutoff).^(2*n))
H.at<float>( i, j ) = 1.0 / ( 1.0+std::pow( radius/cutoff, 2*n ) )
}
}
/// shift 将中心点移到左上角
H = CenterShift(H)
return H
}
Mat CenterShift( const Mat &_src )
{
亩笑运 Mat src = Mat_<float>(_src)
Mat dst = Mat::zeros( src.rows, src.cols, src.type() )
int N = src.rows
int D = src.cols
int *rowIndex = new int[N]
int *colIndex =new int[D]
memset( rowIndex, 0, sizeof(rowIndex[0])*N )
memset( colIndex, 0, sizeof(colIndex[0])*D )
/// 行 顺序
int begin = N/2
for ( int i=0 i<N i++ )
{
rowIndex[i] = begin
begin++
if ( begin>=N )
{
begin = 0
}
}
/// 列 顺序
begin = D/2
for ( int i=0 i<D i++ )
{
colIndex[i] = begin
begin++
if ( begin>=D )
{
begin = 0
}
}
/// 重新排序
for ( int i=0 i<N i++ )
{
for ( int j=0 j<D j++ )
{
dst.at<float>( i, j ) = src.at<float>( rowIndex[i], colIndex[j] )
}
}
/// 释放
delete []rowIndex
delete []colIndex
rowIndex = NULL
colIndex = NULL
return dst
}
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)