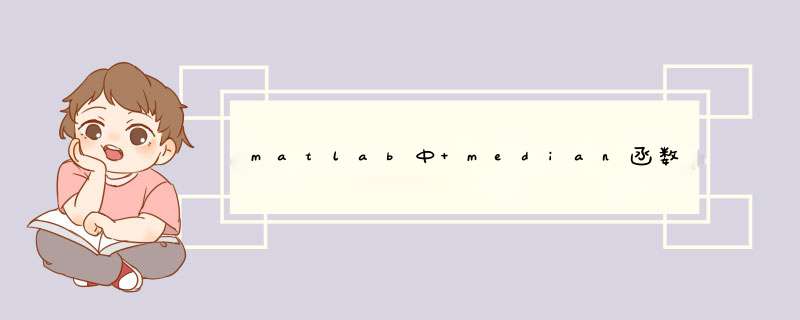
如果元素数量是奇数,取最中间那个元素;
如果元素数量是偶数,取最中间两个元素的算术平均值。
>>edit median
function y = median(x,dim)
%MEDIAN Median value.
% For vectors, MEDIAN(X) is the median value of the elements in X.
% For matrices, MEDIAN(X) is a row vector containing the median
% value of each column. For N-D arrays, MEDIAN(X) is the median
% value of the elements along the first non-singleton dimension
% of X.
%
% MEDIAN(X,DIM) takes the median along the dimension DIM of X.
%
% Example: If X = [0 1 2
%3 4 5]
%
% then median(X,1) is [1.5 2.5 3.5] and median(X,2) is [1
% 4]
%
% Class support for input X:
% float: double, single
%
% See also MEAN, STD, MIN, MAX, VAR, COV, MODE.
% Copyright 1984-2005 The MathWorks, Inc.
% $Revision: 5.15.4.6 $ $Date: 2005/05/31 16:30:47 $
% Calculation method for even lists: b - (b-a)/2.
% This method reduces the likelihood of rounding errors.
nInputs = nargin
if isempty(x)
if nInputs == 1
% The output size for [] is a special case when DIM is not given.
if isequal(x,[]), y = nan(1,class(x))returnend
% Determine first nonsingleton dimension
dim = find(size(x)~=1,1)
end
s = size(x)
if dim <= length(s)
s(dim) = 1 % Set size to 1 along dimension
end
y = nan(s,class(x))
elseif nInputs == 1 &&isvector(x)
% If input is a vector, calculate single value of output.
x = sort(x)
nCompare = numel(x)
half = floor(nCompare/2)
y = x(half+1)
if 2*half == nCompare% Average if even number of elements
y = meanof(x(half),y)
end
if isnan(x(nCompare))% Check last index for NaN
y = nan(class(x))
end
else
if nInputs == 1 % Determine first nonsingleton dimension
dim = find(size(x)~=1,1)
end
s = size(x)
if dim >length(s) % If dimension is too high, just return input.
y = x
return
end
% Sort along given dimension
x = sort(x,dim)
nCompare = s(dim) % Number of elements used to generate a median
half = floor(nCompare/2) % Midway point, used for median calculation
if dim == 1
% If calculating along columns, use vectorized method with column
% indexing. Reshape at end to appropriate dimension.
y = x(half+1,:)
if 2*half == nCompare
y = meanof(x(half,:),y)
end
y(isnan(x(nCompare,:))) = NaN % Check last index for NaN
elseif dim == 2 &&length(s) == 2
% If calculating along rows, use vectorized method only when possible.
% This requires the input to be 2-dimensional. Reshape at end.
y = x(:,half+1)
if 2*half == nCompare
y = meanof(x(:,half),y)
end
y(isnan(x(:,nCompare))) = NaN % Check last index for NaN
else
% In all other cases, use linear indexing to determine exact location
% of medians. Use linear indices to extract medians, then reshape at
% end to appropriate size.
cumSize = cumprod(s)
total = cumSize(end) % Equivalent to NUMEL(x)
numMedians = total / nCompare
numConseq = cumSize(dim - 1) % Number of consecutive indices
increment = cumSize(dim) % Gap between runs of indices
ixMedians = 1
y = repmat(x(1),numMedians,1) % Preallocate appropriate type
% Nested FOR loop tracks down medians by their indices.
for seqIndex = 1:increment:total
for consIndex = half*numConseq:(half+1)*numConseq-1
absIndex = seqIndex + consIndex
y(ixMedians) = x(absIndex)
ixMedians = ixMedians + 1
end
end
% Average in second value if n is even
if 2*half == nCompare
ixMedians = 1
for seqIndex = 1:increment:total
for consIndex = (half-1)*numConseq:half*numConseq-1
absIndex = seqIndex + consIndex
y(ixMedians) = meanof(x(absIndex),y(ixMedians))
ixMedians = ixMedians + 1
end
end
end
% Check last indices for NaN
ixMedians = 1
for seqIndex = 1:increment:total
for consIndex = (nCompare-1)*numConseq:nCompare*numConseq-1
absIndex = seqIndex + consIndex
if isnan(x(absIndex))
y(ixMedians) = NaN
end
ixMedians = ixMedians + 1
end
end
end
% Now reshape output.
s(dim) = 1
y = reshape(y,s)
end
%============================
function c = meanof(a,b)
% MEANOF the mean of A and B with B >A
%MEANOF calculates the mean of A and B. It uses different formula
%in order to avoid overflow in floating point arithmetic.
c = a + (b-a)/2
k = (sign(a) ~= sign(b)) | isinf(a) | isinf(b)
c(k) = (a(k)+b(k))/2
1、matlab是一个功能强大的软件,不仅仅在数据处理方面很优秀,在界面编程方面同样优秀,这里简单介绍下matlab界面编程的基础步骤。
2、在打开的matlab程序中,点击new---graphic user interface,打开创建gui向导--我们选择blank gui,创建空白的gui界面---选择左侧我们需要的控件,如下图,我们选择一个button---将控件拖入到gui界面的合适的位置,双击打开设置属性的界面---设计好界面后,我们先不要编写函数内容,先运行界面---他会提醒我们激活界面将保存界面和代码,我们选择yes---输入文件名,点击保存---我们回到界面编辑界面,点击button右键打开右键菜单,点击view callbacks---callback,来跳转到该控件的回调函数---我们在该函数中输入代码---这时,我们运行程序,点击按钮,即可以在命令窗口中看到button执行的效果。
3、先运行界面,使得matlab给我们创建界面的代码,然后在view callback。
一般的的查询可在matlab里的帮助界面进行搜索,点击帮助。打开帮助页面,左侧检索栏进行检索需要查询的语句,然后即可查看右侧查询结果。
或者在主界面,输入help 空格+你要查询的内容,进行查询。下次你可以尝试一下。
一般程序都会有不懂得语句,或没用过的,可以在刚刚说过的帮助页面进行查询,看如何使用,输入参量什么意义,程序输出结果是什么。
你这个描述太过于简略了,我只能给出这样的答案了,一般可以都给一点程序,也许会有对答题人帮助。
不过你这个程序的确有点复杂,不根据前后逻辑,和主程序和目的是很难解答的。
你可以看看主程序,再查查帮助。
希望对你有所帮助。谢谢。
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)