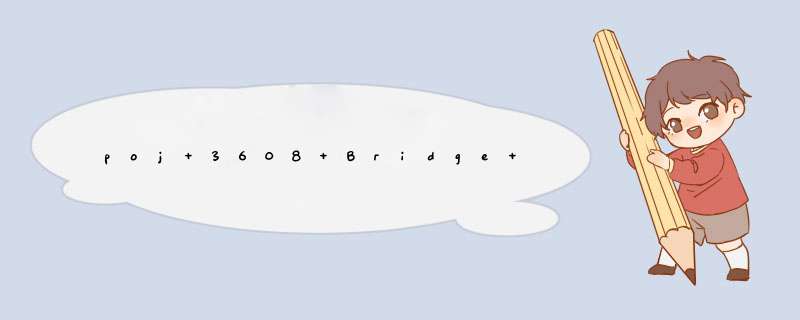
#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cstring>#include <cstdlib>#include <algorithm>#include <cmath>#define N 22222#define PI 3.14159265358979#define EPS 1e-7using namespace std;struct PO{ double x,y;}p1[N],p2[N],o;int n,m,top1,top2,stk1[N],stk2[N];inline int doublecmp(double x){ if(x>EPS) return 1; else if(x<-EPS) return -1; return 0;}inline bool cmp(const PO &a,const PO &b){ if(doublecmp(a.x-b.x)==0) return a.y<b.y; return a.x<b.x;}inline void read(){ for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) scanf("%lf%lf",&p1[i].x,&p1[i].y); for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) scanf("%lf%lf",&p2[i].x,&p2[i].y);}inline PO operator +(PO a,PO b){ PO c; c.x=a.x+b.x; c.y=a.y+b.y; return c;}inline PO operator -(PO a,PO b){ PO c; c.x=a.x-b.x; c.y=a.y-b.y; return c;}inline double dot(PO &a,PO &b,PO &c){ return (b.x-a.x)*(c.x-a.x)+(b.y-a.y)*(c.y-a.y);}inline double cross(PO &a,PO &b,PO &c){ return (b.x-a.x)*(c.y-a.y)-(b.y-a.y)*(c.x-a.x);}inline double getlen(PO &a)//向量的模 { return sqrt(a.x*a.x+a.y*a.y);}inline PO getty(PO b,PO a)//投影向量 { PO res=a; double k=dot(o,a,b)/(getlen(a)*getlen(a)); res.x*=k; res.y*=k; return res;}inline double getangle(PO &a,PO &b,PO&c,PO &d){ PO t=c+(a-d); return cross(a,b,t);}inline PO rotate(PO a,double hd){ PO c; c.x=a.x*cos(hd)-a.y*sin(hd); c.y=a.x*sin(hd)+a.y*cos(hd); return c;}inline double getdis(PO &a,PO &b){ return sqrt((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)+(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y));}inline double getdis_ps(PO &a,PO &b,PO &c){ PO t=c-b; t=rotate(t,-PI*0.5); PO s=c-a;; PO ty=getty(s,t); s=a+ty; if(doublecmp(dot(s,b,c))<=0) return getlen(ty); else return min(getdis(a,b),getdis(a,c));}inline void graham(PO *p,int *stk,int &top,int gs){ sort(p+1,p+1+gs,cmp); top=-1; stk[++top]=1; stk[++top]=2; for(int i=3;i<=gs;i++) { while(top>=1&&doublecmp(cross(p[stk[top-1]],p[stk[top]],p[i]))<=0) top--; stk[++top]=i; } int tmp=top; for(int i=gs-1;i>=1;i--) { while(top>=tmp+1&&doublecmp(cross(p[stk[top-1]],p[stk[top]],p[i]))<=0) top--; stk[++top]=i; }}inline double rotating_calipers(){ int s1=0,s2=0; for(int i=1;i<top1;i++) if(doublecmp(p1[stk1[i]].y-p1[stk1[s1]].y)<0||(doublecmp(p1[stk1[i]].y-p1[stk1[s1]].y)==0)&&doublecmp(p1[stk1[i]].x-p1[stk1[s1]].x)<0) s1=i; for(int i=1;i<top2;i++) if(doublecmp(p2[stk2[i]].y-p2[stk2[s2]].y)>0||(doublecmp(p2[stk2[i]].y-p2[stk2[s2]].y)==0)&&doublecmp(p2[stk2[i]].x-p2[stk2[s2]].x)>0) s2=i; int t1=s1,t2=s2; double ans=getdis(p1[stk1[s1]],p2[stk2[s2]]); do { double af=getangle(p1[stk1[s1]],p1[stk1[(s1+1)%top1]],p2[stk2[s2]],p2[stk2[(s2+1)%top2]]); if(doublecmp(af)==0)//卡壳到两条边 { ans=min(ans,getdis_ps(p1[stk1[s1]],p2[stk2[s2]],p2[stk2[(s2+1)%top2]])); ans=min(ans,getdis_ps(p1[stk1[(s1+1)%top1]],p2[stk2[s2]],p2[stk2[(s2+1)%top2]])); ans=min(ans,getdis_ps(p2[stk2[s2]],p1[stk1[s1]],p1[stk1[(s1+1)%top1]])); ans=min(ans,getdis_ps(p2[stk2[(s2+1)%top2]],p1[stk1[s1]],p1[stk1[(s1+1)%top1]])); s1=(s1+1)%top1; s2=(s2+1)%top2; } else if(doublecmp(af)>0)//卡壳到第一个的边,第二个的点 { ans=min(ans,getdis_ps(p2[stk2[s2]],p1[stk1[s1]],p1[stk1[(s1+1)%top1]])); s1=(s1+1)%top1; } else//卡壳到第二个的边,第一个的点 { ans=min(ans,getdis_ps(p1[stk1[s1]],p2[stk2[s2]],p2[stk2[(s2+1)%top2]])); s2=(s2+1)%top2; } }while(t1!=s1||t2!=s2); return ans;}inline void go(){ graham(p1,stk1,top1,n); graham(p2,stk2,top2,m); printf("%.5lfn",rotating_calipers());}int main(){ while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m),n) read(),go(); return 0;}
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)