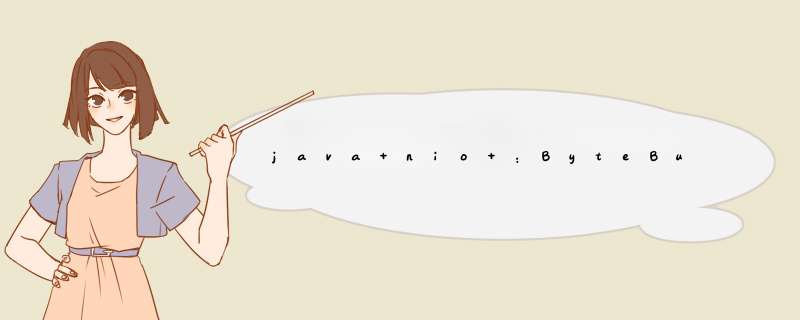
- bytebuffer基本函数
-
// 分配了一个能存储8字节的ByteBuffer,并且只能写入 ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(8);
-
// 由写切换成读 buffer.flip();
-
// 读转写 buffer.clear();
-
- 基本使用流程
- 向buffer写入数据,比如调用channel.read(buffer)
- 调用flip()切换成读模式
- 向buffer读取数据,比如调用buffer.get()
- 调用clear() # 从头开始写或compact() #上次未读完的位置开始写 切换成写模式
- 重复以上步骤
- 内部结构
- 基本属性:
- capcity:容量
- position:读和写的起始指针
- limit:读写位置限制
- limit-position表示可读/写的容量
- 基本属性:
- bytebuffer方法
-
rewind(): // 将position设为0,表示会从0开始读
-
put() # 读数据,position会移动 put(int index) # position不会移动
-
mark() # 记录position位置 reset() #将position重置到mark()那里
-
- 集中读
-
FileChannel channel = new FileInputStream("data.txt").getChannel(); ByteBuffer buffer1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(4); ByteBuffer buffer2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(5); ByteBuffer buffer3 = ByteBuffer.allocate(6); channel.read(new ByteBuffer[]{buffer1, buffer2, buffer3}); buffer1.flip(); buffer2.flip(); buffer3.flip();
-
- 集中写
-
ByteBuffer a = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("hello"); ByteBuffer b = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("world"); ByteBuffer c = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("你好"); try { FileChannel channel = new RandomAccessFile("data2.txt", "rw").getChannel(); channel.write(new ByteBuffer[]{a, b, c}); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
-
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)