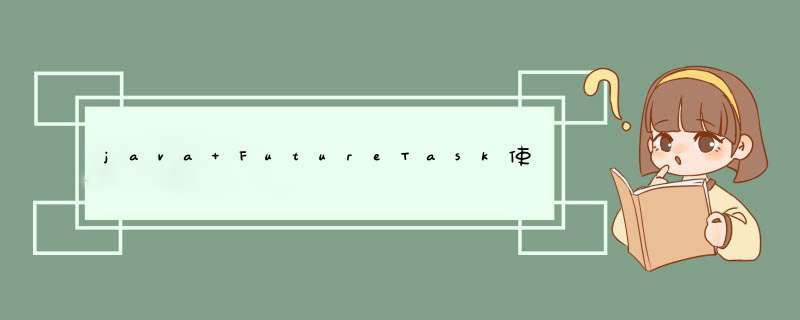
public static Integer getTotal1(){
try {
System.out.println("开始getTotal1");
Thread.sleep(6000);
System.out.println("结束getTotal1");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 1;
}
public static Integer getTotal2(){
try {
System.out.println("开始getTotal2");
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println("结束getTotal2");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 3;
}
使用普通方式调用上面两个方法得到返回数据需要耗时9秒多, 一个方法6秒多,一个方法3秒多,
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.err.print(getTotal1());
System.err.print(getTotal2());
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.err.print("耗时=====>"+(end-start));
使用FutureTask 则只需要6秒多就可以得到两个方法的返回数据
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Callable ca1 = new Callable(){
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return getTotal1();
}
};
FutureTask recharge1 = new FutureTask(ca1);
new Thread(recharge1).start();
Callable ca2 = new Callable(){
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return getTotal2();
}
};
FutureTask recharge2 = new FutureTask(ca2);
new Thread(recharge2).start();
System.err.print(recharge1.get());
System.err.print("n====================n");
System.err.print(recharge2.get());
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.err.print("耗时=====>"+(end-start));
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)