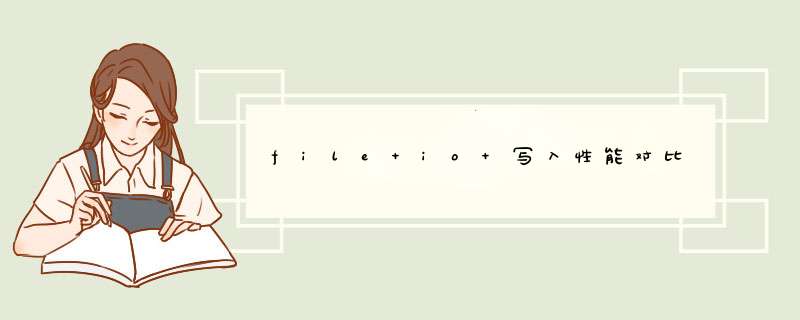
#include#include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #define SIZE 50*1024*1024 int main(int argc, char** argv) { FILE *fp; char c = 'a'; int i; char *pmap; int fd; char *mem; struct timeval t1, t2; long spend_us; printf("write size: %dMBn", SIZE/1024/1024); if((fp = fopen("disk_file", "w")) == NULL) { printf("fopen error!n"); return -1; } gettimeofday(&t1, NULL); for(i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { if(fwrite(&c, sizeof(char), 1, fp) != 1) printf("file write error!n"); } gettimeofday(&t2, NULL); spend_us = 1000000 * (t2.tv_sec - t1.tv_sec) + (t2.tv_usec - t1.tv_usec); printf("write disk file,spend time:%ld usn", spend_us); fclose(fp); fd = open("mmap_file", O_RDWR); if(fd < 0){ perror("open mmap_file"); return -1; } pmap = (char *)mmap(NULL, sizeof(char) * SIZE, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, fd, 0); if(pmap == MAP_FAILED){ perror("mmap"); return -1; } gettimeofday(&t1, NULL); for(i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { memcpy(pmap + i, &c, 1); } gettimeofday(&t2, NULL); spend_us = 1000000 * (t2.tv_sec - t1.tv_sec) + (t2.tv_usec - t1.tv_usec); printf("write mmap file,spend time:%ld usn", spend_us); close(fd); munmap(pmap, sizeof(char) * SIZE); mem = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * SIZE); if(!mem) { printf("mem malloc error!n"); return -1; } gettimeofday(&t1, NULL); for(i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { memcpy(mem + i, &c, 1); } gettimeofday(&t2, NULL); spend_us = 1000000 * (t2.tv_sec - t1.tv_sec) + (t2.tv_usec - t1.tv_usec); printf("write mem,spend time:%ld usn", spend_us); free(mem); return 0; }
1B写入, 50*1024*1024 次
write size: 50MB
write disk file,spend time:790204 us (磁盘文件,只打开一次)
write mmap file,spend time:118592 us
write mem,spend time:118319 us
write disk file,spend time:2833924027 us (磁盘文件,每次写入打开一次)
write mmap file,spend time:121040 us
write mem,spend time:123624 us
总结: 即可通过只打开一次文件一直读写加速,在其他部分代码耗时和写入数据长度确定的情况下可提速。但实际中其他部分的代码性能可能占比更高超过写文件耗时;这时可能只能通过写内存抓数统一导出的方式来提速。
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)