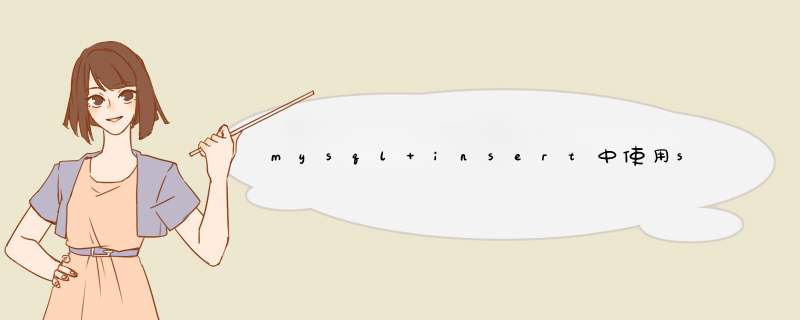
INTO
aa
(a,
b,
c,
d,
e,
f,
g,
h)
SELECT
id
as
a,
title,
c,
d,
e,
f,
g,
h
FROM
b
WHERE
id
=
1
注意:
readset
writeset
exceptset指定要让内核测试读、写和异常条件的描述字。如果对某一个的条件不感兴趣,就可以把它设为NULL。如果三个指针都为NULL,我们就有了一个比sleep()函数更为精确的定时器(sleep()以毫秒为最小单位,这个以微秒为单位)。
select使用描述字集,典型地是一个整数数组,其中每个整数中的每一位对应一个描述字。假设使用32位整数,那么该数组的第一个元素对应于描述字0~31,第二个元素对应于描述字32~63,依此类推。所有的实现细节都与应用程序无关,它们隐藏在名为fd_set的数据类型和以下四个宏中:
void
FD_ZERO
(fd_set
*fdset)
//
clear
all
bits
in
fdset
void
FD_SET
(int
fd,fd_set
*fdset)
//
turn
on
the
bit
for
fd
in
fdset
void
FD_CLR
(int
fd,fd_set
*fdset)
//
turn
off
the
bit
for
fd
in
fdset
intFD_ISSET(int
fd,fd_set
*fdset)
//
is
the
bit
for
fd
on
in
fdset
哎呀, select里没有set你直接select一个常量就行了, 只要位置对应就可以了
select `Year`,`Quarter`,`Month`,"Global","Global",.......
有时候需要把查询到的数据直接插入另一个表中,sql如下:insert into a
(a.aid, a.name)
select id, name from b
where b.xx = xx
更新 *** 作如下:
UPDATE ta SET name = ( SELECT a.name
FROM a
WHERE ta.aid = a.id )
WHERE ta.pid = xx
内容追加:
update ta set name = CONCAT(name, 'str') WHERE id = xx //CONCAT 追加字段内容
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)