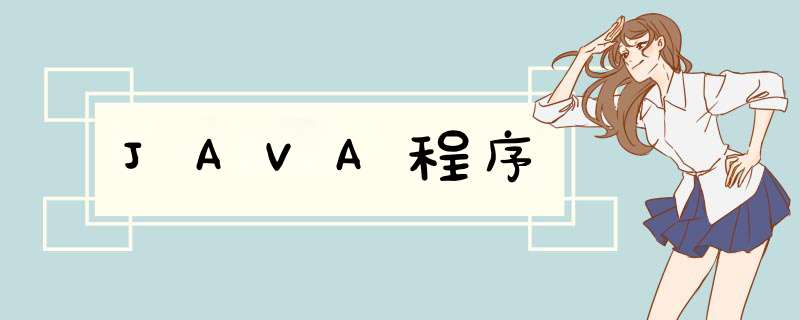
import javautil;
import javaio;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random random = new Random();
BufferedReader br = null;
BufferedWriter bw = null;
int[] array = new int[15];
/
产生15个随机数,并写入到file2txt文件
/
try {
bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("file2txt"));
} catch (IOException e) {
Systemoutprintln("文件找不到!");
eprintStackTrace();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 15; i++) {
try {
int n = randomnextInt(9980) + 20; //20到9999的随机数
bwwrite(StringvalueOf(n)); //将int转换为String并写入到文件
bwnewLine(); //换行
} catch (IOException e) {
Systemoutprintln("文件写入失败!");
eprintStackTrace();
}
}
try {
bwflush();
bwclose();
} catch (IOException e) {
Systemoutprintln("文件关闭失败!");
eprintStackTrace();
}
/
读取file2txt
/
int tem = 0;
String str;
try {
br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("file2txt"));
while ((str = brreadLine()) != null) {
int n = IntegerparseInt(str);
array[tem] = n;
tem++;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
Systemoutprintln("读取文件失败");
eprintStackTrace();
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
Systemoutprintln("读到了非数字符号!");
eprintStackTrace();
}
try {
brclose();
} catch (IOException e) {
Systemoutprintf("关闭文件失败!");
eprintStackTrace();
}
/
排序(选择排序)
/
for (int i = 0; i < arraylength; i++) {
int k = i;
for (int j = k + 1; j < arraylength; j++) {
if (array[j] < array[k]) {
k = j;
}
}
if (k != i) {
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[k];
array[k] = temp;
}
}
for(int i = 0 ;i < 15; i++){
Systemoutprintln(array[i]);
}
}
}
//没有写方法包装,将就这看吧(常用的排序算法其实java包装好了的,可以之间调用)!
下面这个把每个方法各自包装了
import javautil;
import javaio;
public class Test {
Random random = new Random();
BufferedReader br = null;
BufferedWriter bw = null;
int[] array = new int[15];
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test test = new Test();
testtoWriter();
testtoReader();
testrank();
}
/
产生15个随机数,并写入到file2txt文件
/
public void toWriter(){
try {
bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("file2txt"));
} catch (IOException e) {
Systemoutprintln("文件找不到!");
eprintStackTrace();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 15; i++) {
try {
int n = randomnextInt(9980) + 20; //20到9999的随机数
bwwrite(StringvalueOf(n)); //将int转换为String并写入到文件
bwnewLine(); //换行
} catch (IOException e) {
Systemoutprintln("文件写入失败!");
eprintStackTrace();
}
}
try {
bwflush();
bwclose();
} catch (IOException e) {
Systemoutprintln("文件关闭失败!");
eprintStackTrace();
}
}
/
读取file2txt
/
public void toReader(){
int tem = 0;
String str;
try {
br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("file2txt"));
while ((str = brreadLine()) != null) {
int n = IntegerparseInt(str);
array[tem] = n;
tem++;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
Systemoutprintln("读取文件失败");
eprintStackTrace();
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
Systemoutprintln("读到了非数字符号!");
eprintStackTrace();
}
try {
brclose();
} catch (IOException e) {
Systemoutprintf("关闭文件失败!");
eprintStackTrace();
}
}
/
排序(选择排序)
/
public void rank(){
for (int i = 0; i < arraylength; i++) {
int k = i;
for (int j = k + 1; j < arraylength; j++) {
if (array[j] < array[k]) {
k = j;
}
}
if (k != i) {
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[k];
array[k] = temp;
}
}
for(int i = 0 ;i < 15; i++){
Systemoutprintln(array[i]);
}
}
}
方法一:import javautil;
public class ProOne {
//题目:输入两个正整数m和n,求其最大公约数和最小公倍数。
//程序分析:利用辗除法。
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int m=0,n=0,m1=0,n1=0;
int a;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(Systemin);
Systemoutprintln("请输入m的值:");
m=scannernextInt();
Systemoutprintln("请输入n的值:");
n=scannernextInt();
//将输入的m和n值备份;
m1=m;
n1=n;
//取得两个数相除的余数;
a=m%n;
while(a!=0)
{
m1=n1;n1=a;a=m1%n1;
}
Systemoutprintln("m,n的最大公约数为:"+n1);
//求两个数字的最小公倍数的方法为:(两个数的乘积)/(两个数字的最大公约数);
Systemoutprintln("m,n两个数的最小公倍数为:"+mn/n1);
}
}
方法2:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Systemoutprintln(gongyue(10, 12));
}
//迭代n的阶乘
public static int method(int n) {
if (n == 1) {
return 1;
} else {
return n method(n - 1);
}
}
// 求m和n的最大公约数
public static int gongyue(int m, int n) {
while (m % n != 0) {
int temp = m % n;
m = n;
n = temp;
}
return n;
}
// 求m和n的最小公倍数
public static int gongbei(int m, int n) {
return m n / gongyue(m, n);
}
}
package com;
public interface PlaneGraphics {
public abstract double area();
public abstract double perimeter();
public abstract void print();
}
package com;
public class Rectangle implements PlaneGraphics{
private double x = 75;
private double y = 157;
private double s = 0;
private double l= 0;
public double area() {
s = x y;
return s;
}
public double perimeter() {
l = 2 (x + y);
return l;
}
public void print() {
Systemoutprintln("这是长方形");
Systemoutprintln("长方形的宽度:"+x+"长方形的长度:"+y);
Systemoutprintln("长方形的面积:"+s);
Systemoutprintln("长方形的周长:"+l);
}
package com;
public class Ellipse implements PlaneGraphics {
private double a = 57;
private double b = 25;
private double s = 0;
private double l = 0;
private double pie = 314;
public double area() {
s = pie a b;
return s;
}
public double perimeter() {
double m = 0;
m = javalangMathsqrt(a b);
l = pie (15 (a+b) - m);
return l;
}
public void print() {
Systemoutprintln("这是椭圆形");
Systemoutprintln("椭圆形的a轴长:"+a+"椭圆形的b轴长:"+b);
Systemoutprintln("椭圆形的面积:"+s);
Systemoutprintln("椭圆形的周长:"+l);
}
}
package com;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Rectangle rec = new Rectangle();
recarea();
recperimeter();
recprint();
Ellipse ell = new Ellipse();
ellarea();
ellperimeter();
ellprint();
}
}
import javaawt;
import javaapplet;
import javaawtevent;
public class Ex4_1 extends Applet implements ActionListener //本类实现了监听
{
TextField text1=new TextField(10); //产生一个文本框 宽度10
Label lb1=new Label("+");//产生标签
TextField text2=new TextField(10); //产生一个文本框 宽度10
Label lb2=new Label("=");//
TextField text3=new TextField(10); //产生一个文本框 宽度10
Button btn=new Button("相加");
//产生一个按钮 名叫“相加”
public void Init()
{
//讲上面那些控件加到面板上去。。。
add(text1);add(lb1);
add(text2);add(lb2);
add(text3);
add(btn);
btnaddActionListener(this);//给按钮加上监听事件 也就是绑定自己。。。因为本类实现了监听
}
//事件处理方法。。。。
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
int x;
//将两个文本的值转换成整形加在一起付给x
x=Integerparselnt(text1getText())+Integerparselnt(text2getText());
//将x值转换成字符串赋给文本框3
text3setText(IntegertoString(x));
}
}
下面这个程序向大家展示了break和continue在for和while循环中的例子:
//: BreakAndContinuejava
// Demonstrates break and continue keywords
public class BreakAndContinue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
if(i == 74) break; // Out of for loop
if(i % 9 != 0) continue; // Next iteration
Systemoutprintln(i);
}
int i = 0;
// An "infinite loop":
while(true) {
i++;
int j = i 27;
if(j == 1269) break; // Out of loop
if(i % 10 != 0) continue; // Top of loop
Systemoutprintln(i);
}
}
} ///:~
在这个for循环中,i的值永远不会到达100。因为一旦i到达74,break语句就会中断循环。通常,只有在不知道中断条件何时满足时,才需象这样使用break。只要i不能被9整除,continue语句会使程序流程返回循环的最开头执行(所以使i值递增)。如果能够整除,则将值显示出来。
第二部分向大家揭示了一个“无限循环”的情况。然而,循环内部有一个break语句,可中止循环。除此以外,大家还会看到continue移回循环顶部,同时不完成剩余的内容(所以只有在i值能被9整除时才打印出值)。输出结果如下:
0
9
18
27
36
45
54
63
72
10
20
30
40
之所以显示0,是由于0%9等于0。
无限循环的第二种形式是for(;;)。编译器将while(true)与for(;;)看作同一回事。所以具体选用哪个取决于自己的编程习惯。
以上就是关于JAVA程序全部的内容,包括:JAVA程序、12. 编写一个Java 小程序,鼠标点击界面,以该点为中心画一个边长为200的正方形,拖动鼠标正方形跟着动。、求助,用java编写一个小程序等相关内容解答,如果想了解更多相关内容,可以关注我们,你们的支持是我们更新的动力!
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)