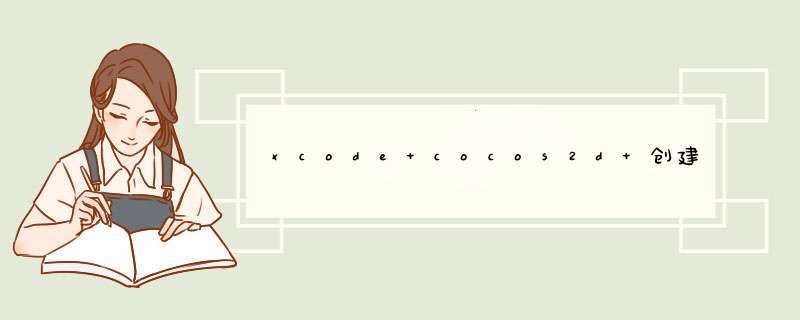
补充:mm文件直接将创建出来的.m文件或者.cpp的后缀改成.mm
1、xcode下的混编,指的的是 C++和 objc之间。而混编的原理就是xcode带了一个 Objective-C++的编译器。这个编译器默认是以 .mm 为后缀的文件为准,所以只要将文件后缀改成.mm,使用的编译器就是这个编译器。.mm的文件中,可以在objc和C++的代码中互相调用嵌套。比如objc的类里面嵌入一个C++的类作为成员,反过来也可以,代码嵌套调用也是可以的。
2、Using C++ With Objective-C
苹果的Objective-C编译器允许用户在同一个源文件里自由地混合使用C++和Objective-C,混编后的语言叫Objective-C++。有了它,你就可以在Objective-C应用程序中使用已有的C++类库。
Objective-C和C++混编的要点
在Objective-C++中,可以用C++代码调用方法也可以从Objective-C调用方法。在这两种语言里对象都是指针,可以在任何地方使用。例如,C++类可以使用Objective-C对象的指针作为数据成员,Objective-C类也可以有C++对象指针做实例变量。下例说明了这一点。
注意:Xcode需要源文件以".mm"为扩展名,这样才能启动编译器的Objective-C++扩展。
例程:
/* Hello.mm* Compile with: g++ -x objective-c++ -framework Foundation Hello.mm -o hello
*/
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
class Hello {
private:
id greeting_text // holds an NSString
public:
Hello() {
greeting_text = @"Hello, world!"
}
Hello(const char* initial_greeting_text) {
greeting_text = [[NSString alloc] initWithUTF8String:initial_greeting_text]
}
void say_hello() {
printf("%s/n", [greeting_text UTF8String])
}
}
@interface Greeting : NSObject {
@private
Hello *hello
}
- (id)init
- (void)dealloc
- (void)sayGreeting
- (void)sayGreeting:(Hello*)greeting
@end
@implementation Greeting
- (id)init {
if (self = [super init]) {
hello = new Hello()
}
return self
}
- (void)dealloc {
delete hello
[super dealloc]
}
- (void)sayGreeting {
hello->say_hello()
}
- (void)sayGreeting:(Hello*)greeting {
greeting->say_hello()
}
@end
int main() {
NSAutoreleasePool *pool = [[NSAutoreleasePool alloc] init]
Greeting *greeting = [[Greeting alloc] init]
[greeting sayGreeting] // > Hello, world!
Hello *hello = new Hello("Bonjour, monde!")
[greeting sayGreeting:hello] // > Bonjour, monde!
delete hello
[greeting release]
[pool release]
return 0
}
.打开Xcode的某一个工程 .添加头文件依次找到Header Search Paths: 添加#include <>的路径
User Header Search Paths: 添加#include “”路径
4.添加库文件
Library Search Paths: 添加库所在目录
Other Linker Flags: 比如要链接的库是libboost_regex.a,那么此处应该添加-lboost_regex即可。
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)