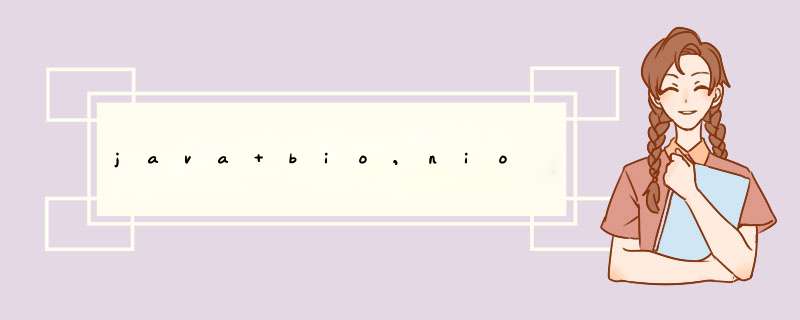
先来了解几个关键词:
1、DMA控制器:通俗来讲,就是 *** 作内存和硬盘之间数据的复制,可以让当前线程释放CPU,在DMA出来之前,是由CPU来做这事的
2、pageCache:就是一个高速缓冲区,缓存IO(大部分IO *** 作都是缓存IO)中用户态和内核态之间的一个桥梁
3、缓存IO,直接IO
缓存IO:大部分IO使用的一种方式
4、mmap:就是用户进程虚拟内存地址和内核内存间直接建立映射关系,用户态可以直接访问内核态内存中的数据,且访问磁盘文件时无需再进行系统调用
5、sendfile:可以把pageCache中的数据直接发给网关/磁盘文件,即两个文件描述符之间可以直接进行数据复制,实现了真正的零拷贝
BIO
先来看下用bio进行socket通信代码:
socket client:
public static void bioSend(Path filename) throws IOException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1",8888);
BufferedOutputStream outputStream = new BufferedOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
try (BufferedInputStream fileInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(filename.toFile()))) {
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024*1024*10];
while (fileInputStream.read(bytes) != -1){
outputStream.write(bytes);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("bio执行耗时:"+(end-start));
}socket server:
public class SocketServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(8888);
System.out.println("启动服务器....");
Socket s = ss.accept();
BufferedInputStream inputStream = new BufferedInputStream(s.getInputStream());
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024*1024*10];
while (inputStream.read(bytes) != -1){
System.out.println(bytes.length);
}
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}传统fileInputStream.read(bytes) != -1调用了read0本地方法,进行了一次系统调用
private native int read0() throws IOException;在outputStream.write(bytes);调用了socketWrite0本地方法,进行了一次系统调用
private native void socketWrite0(FileDescriptor fd, byte[] b, int off,
int len) throws IOException;在代码中 fileInputStream.read(bytes) 把pageCache的数据copy到byte数组中是cpu *** 作
outputStream.write(bytes);把数组中的数据copy到socket也是cpu *** 作
则:
1、发生了两次系统调用,4次用户态和内核态上下文切换,一次系统调用两次上下文切换
2、两次DMA copy和两次CPU copy
nio-内存映射MappedByteBuffer
先来看下用MappedByteBuffer进行socket通信代码:
socket client:
public static void mappedFile(Path filename) throws IOException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//1.打开通道
SocketChannel socketChannel=SocketChannel.open();
//2.连接指定ip和端口号
socketChannel.connect (new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",8888));
//3.写出数据
try (FileChannel fileChannel = FileChannel.open(filename)) {
long size = fileChannel.size();//2147483647
MappedByteBuffer mappedByteBuffer = fileChannel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_ONLY, 0, size);
socketChannel.write(mappedByteBuffer);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//4.释放资源
socketChannel.close();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("mappedFile执行耗时:"+(end-start));
}socket server:
public class NioSocketServer {
static List channelList = new ArrayList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
int size = 0;
// 创建NIO ServerSocketChannel,与BIO的serverSocket类似
ServerSocketChannel serverSocket = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocket.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(8888));
// 设置ServerSocketChannel为非阻塞
serverSocket.configureBlocking(false);
System.out.println("服务启动成功");
while (true) {
// 非阻塞模式accept方法不会阻塞,否则会阻塞
// NIO的非阻塞是由 *** 作系统内部实现的,底层调用了linux内核的accept函数
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocket.accept();
if (socketChannel != null) {
// 如果有客户端进行连接
System.out.println("连接成功");
// 设置SocketChannel为非阻塞
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 保存客户端连接在List中
channelList.add(socketChannel);
}
// 遍历连接进行数据读取
Iterator iterator = channelList.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SocketChannel sc = iterator.next();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024*1024*10);
// 非阻塞模式read方法不会阻塞,否则会阻塞
int len = sc.read(byteBuffer);
if(len > 0){
size += len;
System.out.println(len);
System.out.println("size:"+size);
}
}
}
}
}
fileChannel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_ONLY, 0, size);中发生了一次系统调用
private native long map0(int var1, long var2, long var4) throws IOException;socketChannel.write(mappedByteBuffer);中发生了一次系统调用
static native int pwrite0(FileDescriptor var0, long var1, int var3, long var4) throws IOException;socketChannel.write(mappedByteBuffer);用户进行需要获取到这个内存映射数据块,放入到socket缓存区中,这块是需要CPU来 *** 作的
则:
1、发生了两次系统调用,4次用户态和内核态上下文切换
2、两次DMA copy和一次CPU copy
nio-sendfile
先来看下用sendfile进行socket通信代码:
socket client:
//默认一次传8M 加-Djdk.nio.enableFastFileTransfer=true
public static void sendFile(Path filename) throws IOException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//1.打开通道
SocketChannel socketChannel=SocketChannel.open();
//2.连接指定ip和端口号
socketChannel.connect (new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",8888));
try (FileChannel fileChannel = FileChannel.open(filename)) {
long size = fileChannel.size();
fileChannel.transferTo(0,size,socketChannel);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
socketChannel.close();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("sendFile执行耗时:"+(end-start));
}socket server和上述一样:
private native long transferTo0(FileDescriptor var1, long var2, long var4, FileDescriptor var6);var1:文件描述符,var2:数据的初始偏移量,var4:数据的结束偏移量
var6就是下面socket通道获取的文件描述符
则:
1、发生了一次系统调用,2次用户态和内核态上下文切换
2、两次DMA copy和0次CPU copy
以上都是基于pageCache,pageCache只适合小文件,小文件可以增加命中率,命中成功就无需读取磁盘文件,如果是大文件,则会把pageCahe装满,其他文件进不来,就违背了pageCache设计的初衷,则传输大文件,需要直接IO,AIO中就是用直接IO进行传输的
AIO
先来看下用AIO进行socket通信代码:
socket client:
public static void aioSend(Path filename) {
try {
// 打开一个SocketChannel通道并获取AsynchronousSocketChannel实例
AsynchronousSocketChannel client = AsynchronousSocketChannel.open();
AsynchronousFileChannel channel = AsynchronousFileChannel.open(filename);
System.out.println(channel.size());
// 连接到服务器并处理连接结果
client.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8888), null, new CompletionHandler() {
@Override
public void completed(final Void result, final Void attachment) {
System.out.println("成功连接到服务器!");
try {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024*1024*10);
final int[] num = {0};
while (num[0] < channel.size()){
Future rresult = channel.read(buffer, num[0]);
Future finalRresult = rresult;
num[0] = num[0] + finalRresult.get();
client.write(buffer);
buffer.clear();
System.out.println(result+"-------"+num[0]);
if(num[0] < 0){
break;
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void failed(final Throwable exc, final Void attachment) {
exc.printStackTrace();
}
});
TimeUnit.MINUTES.sleep(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
} catch (IOException | InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} socket server:
package com.fen.dou;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.CompletionHandler;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class AioServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
final int[] size = {0};
final int port = 8888;
//首先打开一个ServerSocket通道并获取AsynchronousServerSocketChannel实例:
AsynchronousServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open();
//绑定需要监听的端口到serverSocketChannel:
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
//实现一个CompletionHandler回调接口handler,
//之后需要在handler的实现中处理连接请求和监听下一个连接、数据收发,以及通信异常。
CompletionHandler handler = new CompletionHandler() {
@Override
public void completed(final AsynchronousSocketChannel result, final Object attachment) {
// 继续监听下一个连接请求
serverSocketChannel.accept(attachment, this);
try {
System.out.println("接受了一个连接:" + result.getRemoteAddress()
.toString());
// 给客户端发送数据并等待发送完成
result.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("From Server:Hello i am server".getBytes()))
.get();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024*1024*10);
Future len = result.read(byteBuffer);
if(len.get() > 0){
size[0] += len.get();
System.out.println(len);
}
System.out.println("size:"+ size[0]);
} catch (IOException | InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void failed(final Throwable exc, final Object attachment) {
System.out.println("出错了:" + exc.getMessage());
}
};
serverSocketChannel.accept(null, handler);
// 由于serverSocketChannel.accept(null, handler);是一个异步方法,调用会直接返回,
// 为了让子线程能够有时间处理监听客户端的连接会话,
// 这里通过让主线程休眠一段时间(当然实际开发一般不会这么做)以确保应用程序不会立即退出。
TimeUnit.MINUTES.sleep(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
} catch (InterruptedException | IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Future
int var13 = WindowsAsynchronousFileChannelImpl.readFile(WindowsAsynchronousFileChannelImpl.this.handle, var4, this.rem, this.position, var2);client.write(buffer); 发生一次系统调用
int var12 = WindowsAsynchronousSocketChannelImpl.write0(WindowsAsynchronousSocketChannelImpl.this.handle, this.numBufs, WindowsAsynchronousSocketChannelImpl.this.writeBufferArray, var1);则:
1、发生了两次系统调用,4次用户态和内核态上下文切换
2、一次DMA 异步copy,一次DMA 同步copy和1次CPU 异步copy
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)