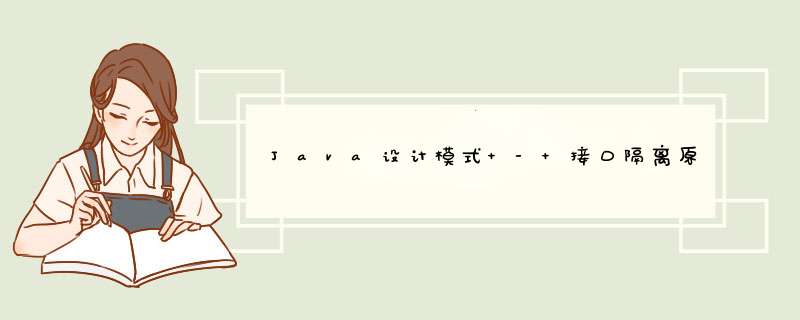
- 1. 违反接口隔离原则
- 2. 遵守接口隔离原则
Interface Segregation Principle:
客户端不应该依赖它不需要的接 口,即一个类对另一个类的依赖应该建立在最小的接口上 。
如下图:类A通过接口Interface1依赖类B,类C通过 接口Interface1依赖类D,如果接口 Interface1对于类A和类C来说不是最小接口, 那么类B和类D必须去实现他们不需要的方法。
interface Interface1 {
void operation1();
void operation2();
void operation3();
void operation4();
void operation5();
}
类B实现Interface1 :
class B implements Interface1 {
@Override
public void operation1() {
System.out.println("B 实现了 operation1");
}
@Override
public void operation2() {
System.out.println("B 实现了 operation2");
}
@Override
public void operation3() {
System.out.println("B 实现了 operation3");
}
@Override
public void operation4() {
System.out.println("B 实现了 operation4");
}
@Override
public void operation5() {
System.out.println("B 实现了 operation5");
}
}
类D实现了Interface1:
class D implements Interface1 {
@Override
public void operation1() {
System.out.println("D 实现了 operation1");
}
@Override
public void operation2() {
System.out.println("D 实现了 operation2");
}
@Override
public void operation3() {
System.out.println("D 实现了 operation3");
}
@Override
public void operation4() {
System.out.println("D 实现了 operation4");
}
@Override
public void operation5() {
System.out.println("D 实现了 operation5");
}
}
A 类通过接口Interface1 依赖(使用) B类,但是只会用到1,2,3方法:
class A {
public void depend1(Interface1 i) {
i.operation1();
}
public void depend2(Interface1 i) {
i.operation2();
}
public void depend3(Interface1 i) {
i.operation3();
}
}
C 类通过接口Interface1 依赖(使用) D类,但是只会用到1,4,5方法:
class C {
public void depend1(Interface1 i) {
i.operation1();
}
public void depend4(Interface1 i) {
i.operation4();
}
public void depend5(Interface1 i) {
i.operation5();
}
}
类A通过接口Interface1依赖类B,类C通过接口Interface1依赖类D,如果接口 Interface1对于类A和类C来说不是最小接口,那么类B和类D必须去实现他们不需要的方法
2. 遵守接口隔离原则将接口Interface1拆分为独立的几个接口,类A和类C分别与他们需要的接口建立依赖关系。也就是采用接口隔离原则:
将interface1拆分为3个接口:
// 接口1
interface Interface1 {
void operation1();
}
// 接口2
interface Interface2 {
void operation2();
void operation3();
}
// 接口3
interface Interface3 {
void operation4();
void operation5();
}
接口B实现Interface1, Interface2
class B implements Interface1, Interface2 {
@Override
public void operation1() {
System.out.println("B 实现了 operation1");
}
@Override
public void operation2() {
System.out.println("B 实现了 operation2");
}
@Override
public void operation3() {
System.out.println("B 实现了 operation3");
}
}
接口D实现Interface1, Interface3
class D implements Interface1, Interface3 {
@Override
public void operation1() {
System.out.println("D 实现了 operation1");
}
@Override
public void operation4() {
System.out.println("D 实现了 operation4");
}
@Override
public void operation5() {
System.out.println("D 实现了 operation5");
}
}
A 类通过接口Interface1,Interface2 依赖(使用) B类,但是只会用到1,2,3方法
class A {
public void depend1(Interface1 i) {
i.operation1();
}
public void depend2(Interface2 i) {
i.operation2();
}
public void depend3(Interface2 i) {
i.operation3();
}
}
C 类通过接口Interface1,Interface3 依赖(使用) D类,但是只会用到1,4,5方法
class C {
public void depend1(Interface1 i) {
i.operation1();
}
public void depend4(Interface3 i) {
i.operation4();
}
public void depend5(Interface3 i) {
i.operation5();
}
}
测试:
public class Segregation1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a = new A();
a.depend1(new B());
a.depend2(new B());
a.depend3(new B());
C c = new C();
c.depend1(new D());
c.depend4(new D());
c.depend5(new D());
}
}
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)