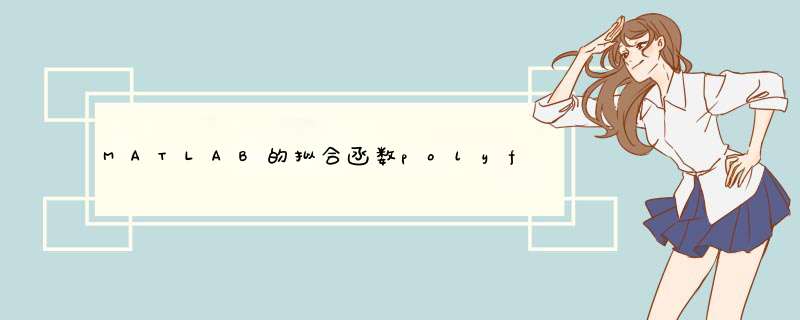
function [p,S,mu] = polyfit(x,y,n)
%POLYFIT Fit polynomial to data.
% P = POLYFIT(X,Y,N) finds the coefficients of a polynomial P(X) of
% degree N that fits the data Y best in a least-squares sense. P is a
% row vector of length N+1 containing the polynomial coefficients in
% descending powers, P(1)*X^N + P(2)*X^(N-1) +...+ P(N)*X + P(N+1).
%
% [P,S] = POLYFIT(X,Y,N) returns the polynomial coefficients P and a
% structure S for use with POLYVAL to obtain error estimates for
% predictions. S contains fields for the triangular factor (R) from a QR
% decomposition of the Vandermonde matrix of X, the degrees of freedom
% (df), and the norm of the residuals (normr). If the data Y are random,
% an estimate of the covariance matrix of P is (Rinv*Rinv')*normr^2/df,
% where Rinv is the inverse of R.
%
% [P,S,MU] = POLYFIT(X,Y,N) finds the coefficients of a polynomial in
% XHAT = (X-MU(1))/MU(2) where MU(1) = MEAN(X) and MU(2) = STD(X). This
% centering and scaling transformation improves the numerical properties
% of both the polynomial and the fitting algorithm.
%
% Warning messages result if N is >= length(X), if X has repeated, or
% nearly repeated, points, or if X might need centering and scaling.
%
% Class support for inputs X,Y:
% float: double, single
%
% See also POLY, POLYVAL, ROOTS.
% Copyright 1984-2004 The MathWorks, Inc.
% $Revision: 5.17.4.5 $ $Date: 2004/07/05 17:01:37 $
% The regression problem is formulated in matrix format as:
%
%y = V*por
%
% 3 2
%y = [x x x 1] [p3
% p2
% p1
% p0]
%
% where the vector p contains the coefficients to be found. For a
% 7th order polynomial, matrix V would be:
%
% V = [x.^7 x.^6 x.^5 x.^4 x.^3 x.^2 x ones(size(x))]
if ~isequal(size(x),size(y))
error('MATLAB:polyfit:XYSizeMismatch',...
'X and Y vectors must be the same size.')
end
x = x(:)
y = y(:)
if nargout >2
mu = [mean(x)std(x)]
x = (x - mu(1))/mu(2)
end
% Construct Vandermonde matrix.
V(:,n+1) = ones(length(x),1,class(x))
for j = n:-1:1
V(:,j) = x.*V(:,j+1)
end
% Solve least squares problem.
[Q,R] = qr(V,0)
ws = warning('off','all')
p = R\(Q'*y) % Same as p = V\y
warning(ws)
if size(R,2) >size(R,1)
warning('MATLAB:polyfit:PolyNotUnique', ...
'Polynomial is not uniquedegree >= number of data points.')
elseif condest(R) >1.0e10
if nargout >2
warning('MATLAB:polyfit:RepeatedPoints', ...
'Polynomial is badly conditioned. Remove repeated data points.')
else
warning('MATLAB:polyfit:RepeatedPointsOrRescale', ...
['Polynomial is badly conditioned. Remove repeated data points\n' ...
' or try centering and scaling as described in HELP POLYFIT.'])
end
end
r = y - V*p
p = p.' % Polynomial coefficients are row vectors by convention.
% S is a structure containing three elements: the triangular factor from a
% QR decomposition of the Vandermonde matrix, the degrees of freedom and
% the norm of the residuals.
S.R = R
S.df = length(y) - (n+1)
S.normr = norm(r)
/***********************************************Author :wacs5
*DATE :20090408(YYYMMDD)
*Functtion :多项式拟合polyfit
**********************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
main()
{
int i,j,m,n=7,poly_n=2
double x[7]={1,2,3,4,6,7,8},y[7]={2,3,6,7,5,3,2}
double a[3]
void polyfit(int n,double *x,double *y,int poly_n,double a[])
system("cls")
polyfit(n,x,y,poly_n,a)
for (i=0i<poly_n+1i++)/*这里是升序排列,Matlab是降序排列*/
printf("a[%d]=%g\n",i,a[i])
getch()
}
/*==================polyfit(n,x,y,poly_n,a)===================*/
/*=======拟合y=a0+a1*x+a2*x^2+……+apoly_n*x^poly_n========*/
/*=====n是数据个数 xy是数据值 poly_n是多项式的项数======*/
/*===返回a0,a1,a2,……a[poly_n],系数比项数多一(常数项)=====*/
void polyfit(int n,double x[],double y[],int poly_n,double a[])
{
int i,j
double *tempx,*tempy,*sumxx,*sumxy,*ata
void gauss_solve(int n,double A[],double x[],double b[])
tempx=calloc(n,sizeof(double))
sumxx=calloc(poly_n*2+1,sizeof(double))
tempy=calloc(n,sizeof(double))
sumxy=calloc(poly_n+1,sizeof(double))
ata=calloc((poly_n+1)*(poly_n+1),sizeof(double))
for (i=0i<ni++)
{
tempx[i]=1
tempy[i]=y[i]
}
for (i=0i<2*poly_n+1i++)
for (sumxx[i]=0,j=0j<nj++)
{
sumxx[i]+=tempx[j]
tempx[j]*=x[j]
}
for (i=0i<poly_n+1i++)
for (sumxy[i]=0,j=0j<nj++)
{
sumxy[i]+=tempy[j]
tempy[j]*=x[j]
}
for (i=0i<poly_n+1i++)
for (j=0j<poly_n+1j++)
ata[i*(poly_n+1)+j]=sumxx[i+j]
gauss_solve(poly_n+1,ata,a,sumxy)
free(tempx)
free(sumxx)
free(tempy)
free(sumxy)
free(ata)
}
void gauss_solve(int n,double A[],double x[],double b[])
{
int i,j,k,r
double max
for (k=0k<n-1k++)
{
max=fabs(A[k*n+k])/*find maxmum*/
r=k
for (i=k+1i<n-1i++)
if (max<fabs(A[i*n+i]))
{
max=fabs(A[i*n+i])
r=i
}
if (r!=k)
for (i=0i<ni++) /*change array:A[k]&A[r] */
{
max=A[k*n+i]
A[k*n+i]=A[r*n+i]
A[r*n+i]=max
}
max=b[k] /*change array:b[k]&b[r] */
b[k]=b[r]
b[r]=max
for (i=k+1i<ni++)
{
for (j=k+1j<nj++)
A[i*n+j]-=A[i*n+k]*A[k*n+j]/A[k*n+k]
b[i]-=A[i*n+k]*b[k]/A[k*n+k]
}
}
for (i=n-1i>=0x[i]/=A[i*n+i],i--)
for (j=i+1,x[i]=b[i]j<nj++)
x[i]-=A[i*n+j]*x[j]
}
有两种方法可以画平滑曲线,第一种是拟合的方法,第二种是用spcrv。
其实原理应该都一样就是插值。下面是源程序,大家可以根据需要自行选择,更改拟合的参数。
clc,clear
a = 1:1:6 %横坐标
b = [8.0 9.0 10.0 15.0 35.0 40.0]%纵坐标
plot(a, b, 'b') %自然状态的画图效果
hold on
%第一种,画平滑曲线的方法
c = polyfit(a, b, 2) %进行拟合,c为2次拟合后的系数
d = polyval(c, a, 1) %拟合后,每一个横坐标对应的值即为d
plot(a, d, 'r') %拟合后的曲线
plot(a, b, '*') %将每个点 用*画出来
hold on
%第二种,画平滑曲线的方法
values = spcrv([[a(1) a a(end)][b(1) b b(end)]],3)
plot(values(1,:),values(2,:), 'g')
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)