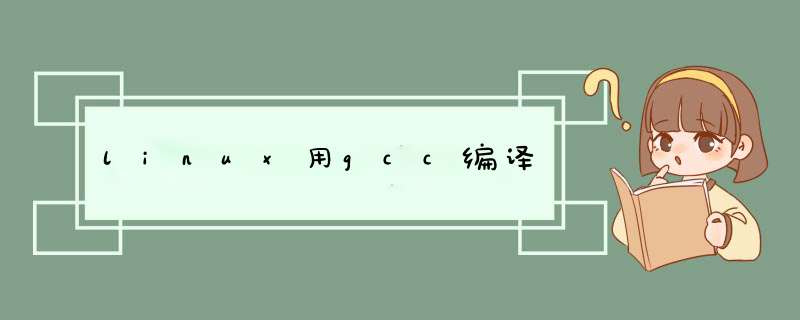
直接编译:
gcc main.c compute.c input.c -o power
运行程序
./power
makefile 最简单,直观的的编写方法:
power:main.o compute.o input.o
cc main.o compute.o input.o -o power
main.o:main.c main.h compute.h input.h
cc -c main.c
compute.o:compute.c compute.h
cc -c compute.c
input.o:input.c input.h
cc -c input.c
.PHONY : clean
clean :
rm -f *.o power
保存后成makefile或Makefile推荐使用后者:
make
想重新编译前运行:
make clean
make
运行程序:
./power
特别说明:cc,rm命令行前有一个tab符,别搞错了。cc 在linux上是指向gcc的软符号链接,为了兼容其他系统,我们写的cc。
makefile有更简写但不简单的写法,不给出来。你提问这个说明你不会编写makefile,给出的是最基本用法。有兴趣自己看,一天能学完。
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char file_name[64] = {0}
char file_path[128] = {0}
char dir_path[64] = {0}
char cmd[256] = {0}
int re = 0
FILE *pf = NULL
char *p = NULL
printf("请输入文件名:\n")
scanf("%s", file_name)
snprintf(cmd, 256, "find -name %s > tmp.txt", file_name)//如果文件不在程序运行的本地目录(或者子目录)下,则需要改成find / -name xxxx 但耗时会很长
system(cmd)
//文件中取绝对路径
pf = fopen("tmp.txt", "r")
if (pf)
{
re = fscanf(pf, "%s", file_path)//只取第一行 也就是默认不存在同名文件
if (-1 == re)
{
printf("err0\n")
return 0
}
else
{
flcose(pf)
pf = NULL
}
}
else
{
printf("err1\n")
return 0
}
if (0 == strlen(file_path))
{
printf("err2\n")
return 0
}
//获取目录名
p = strstr(file_path, file_name)
if (p)
{
*p = '\0'
strcpy(dir_path, file_path)//也可以不cp直接用file_path
}
//通过c语言展开ls这个路径c语言变量 其实我没有理解这句话... 先这么做吧
snprintf(cmd, 256, "ls %s", dir_path)
system(cmd)
return 0
}
如果哪里有异常就加printf打印出来各个变量
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)