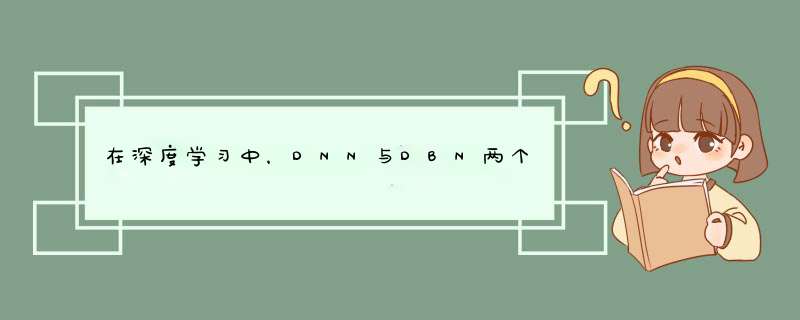
他是一个 有监督的判别模型。
stacked denoised autoencoder (SDA)深度学习结构,和DBN类似 使用 无监督的网络“堆叠”起来的,他有分层预训练来寻找更好的参数,最后使用BP来微调网络。比dnn利用各种消知算法来初始化权值矩阵,从经验上来看是有帮助的。但是缺点也很明显,每层的贪婪学习权值矩阵,也带来了过长的训练时间。在大量的数据面前 dnn(relu)的效果已经不差于预训练的深度学习结构了。最终DBN也是看成是“生成模型”。
CNN 也没有pre-train过程,训练算法也是用BP。 因为加入卷积启迟 可以更好的处理2D数据,例如图像和语音。并且目前看来 相比其它网络有更好的表现。dnn/dbn/sda 等都是处理1D的数据。
如何开启深度学习之旅?这三大类125篇论文为你导航(附资源下载)
如果你现在还是个深度学习的新手,那么你问的第一个问题可能是「我应该从哪篇文章开始读呢?在 G上,s准备了一套深度学习阅读清单,而且这份清单在随时更新。
项目地址:
这份清单依照下述 4 条原则建立:
从整体轮廓到细节
从过去到当代
从一般到具体领域
聚焦当下最先进技术
你会发现很多非常新但很值得一读的论文。这份清单我会持续更新。
1、深度学习的历史与基础知识
1.0 书籍
[0] Bengio, Yoshua, Ian J. Goodfellow, and Aaron Courville. 深度学习(Deep learning), An MIT Press book. (2015). (这是深度学习领域的圣经,你可以在读此书的同时阅读下面的论文)。
1.1 调查类:
[1] LeCun, Yann, Yoshua Bengio, and Geoffrey Hinton. 深度学习 (Deep learning), Nature 521.7553 (2015): 436-444. (深度学习三位大牛对各种学习模型的评价)
1.2 深度信念网络(DBN)(深度学习前夜的里程碑)
[2] Hinton, Geoffrey E., Simon Osindero, and Yee-Whye Teh. 一个关于深度信念网络的快速学习算法(A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets), (深度学习的前夜)
[3] Hinton, Geoffrey E., and Ruslan R. Salakhutdinov. 使用神经网络降低数据的维度(Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks), (里程碑式的论文,展示了深度学习的可靠性蚂裂高)
1.3 ImageNet 的演化(深度学习从这里开始)
[4] Krizhevsky, Alex, Ilya Sutskever, and Geoffrey E. Hinton. 使用深度卷积神经网络进行 ImageNet 分类任务(Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks)(AlexNet, 深度学习的突破)
[5] Simonyan, Karen, and Andrew Zisserman. 针对大尺度图像识别工作的的超深卷积网络(Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition) (VGGNet, 神经网络开始变得非常深!)
[6] Szegedy, Christian, et al. 更深的卷源肆积(Going deeper with convolutions)(GoogLeNet)
[7] He, Kaiming, et al. 图像识别的深度残差学习(Deep residual learning for image recognition)(ResNet,超级超级深的深度网络!CVPR--IEEE 国际计算机视觉与模式识别会议-- 最佳论文)
1.4 语音识别的演化
[8] Hinton, Geoffrey, et al. 语音识别中深度神经网络的声学建模(Deep neural networks for acoustic modeling in speech recognition: The shared views of four research groups)(语音识别中的突破)
[9] Graves, Alex, Abdel-rahman Mohamed, and Geoffrey Hinton. 用深度循环神闷尺经网络进行语音识别(Speech recognition with deep recurrent neural networks)(RNN)
[10] Graves, Alex, and Navdeep Jaitly. 面向端到端语音识别的循环神经网络(Towards End-To-End Speech Recognition with Recurrent Neural Networks)
[11] Sak, Ha?im, et al. 语音识别中快且精准的循环神经网络声学模型(Fast and accurate recurrent neural network acoustic models for speech recognition)(语音识别系统)
[12] Amodei, Dario, et al. Deep speech 2:英语和汉语的端到端语音识别(Deep speech 2: End-to-end speech recognition in english and mandarin)(百度语音识别系统)
[13] W. Xiong, J. Droppo, X. Huang, F. Seide, M. Seltzer, A. Stolcke, D. Yu, G. Zweig,在对话语音识别中实现人类平等(Achieving Human Parity in Conversational Speech Recognition)
当你读完了上面给出的论文,你会对深度学习历史有一个基本的了解,深度学习建模的基本架构(包括了 CNN,RNN,LSTM)以及深度学习如何可以被应用于图像和语音识别问题。下面的论文会让你对深度学习方法,不同应用领域中的深度学习技术和其局限有深度认识。
2 深度学习方法
2.1 模型
[14] Hinton, Geoffrey E., et al. 通过避免特征检测器的共适应来改善神经网络(Improving neural networks by preventing co-adaptation of feature detectors)(Dropout)
[15] Srivastava, Nitish, et al. Dropout:一种避免神经网络过度拟合的简单方法(Dropout: a simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting)
[16] Ioffe, Sergey, and Christian Szegedy. Batch normalization:通过减少内部协变量加速深度网络训练(Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift)(2015 年一篇杰出论文)
[17] Ba, Jimmy Lei, Jamie Ryan Kiros, and Geoffrey E. Hinton.层归一化(Layer normalization)(批归一化的升级版)
[18] Courbariaux, Matthieu, et al. 二值神经网络:训练神经网络的权重和激活约束到正 1 或者负 1(Binarized Neural Networks: Training Neural Networks with Weights and Activations Constrained to+ 1 or?1)(新模型,快)
[19] Jaderberg, Max, et al. 使用合成梯度的解耦神经接口(Decoupled neural interfaces using synthetic gradients)(训练方法的发明,令人惊叹的文章)
[20] Chen, Tianqi, Ian Goodfellow, and Jonathon Shlens. Net2net:通过知识迁移加速学习(Net2net: Accelerating learning via knowledge transfer) (修改之前的训练网络以减少训练)
[21] Wei, Tao, et al. 网络形态(Network Morphism)(修改之前的训练网络以减少训练 epoch)
2.2 优化
[22] Sutskever, Ilya, et al. 有关深度学习中初始化与动量因子的研究(On the importance of initialization and momentum in deep learning) (动量因子优化器)
[23] Kingma, Diederik, and Jimmy Ba. Adam:随机优化的一种方法(Adam: A method for stochastic optimization)(可能是现在用的最多的一种方法)
[24] Andrychowicz, Marcin, et al. 通过梯度下降学习梯度下降(Learning to learn by gradient descent by gradient descent) (神经优化器,令人称奇的工作)
[25] Han, Song, Huizi Mao, and William J. Dally. 深度压缩:通过剪枝、量子化训练和霍夫曼代码压缩深度神经网络(Deep compression: Compressing deep neural network with pruning, trained quantization and huffman coding) (ICLR 最佳论文,来自 DeePhi 科技初创公司,加速 NN 运行的新方向)
[26] Iandola, Forrest N., et al. SqueezeNet:带有 50x 更少参数和小于 1MB 模型大小的 AlexNet-层级精确度(SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level accuracy with 50x fewer parameters and<1MB model size.) (优化 NN 的另一个新方向,来自 DeePhi 科技初创公司)
2.3 无监督学习/深度生成模型
[27] Le, Quoc V. 通过大规模无监督学习构建高级特征(Building high-level features using large scale unsupervised learning.) (里程碑,吴恩达,谷歌大脑,猫)
[28] Kingma, Diederik P., and Max Welling. 自动编码变异贝叶斯(Auto-encoding variational bayes.) (VAE)
[29] Goodfellow, Ian, et al. 生成对抗网络(Generative adversarial nets.)(GAN, 超酷的想法)
[30] Radford, Alec, Luke Metz, and Soumith Chintala. 带有深度卷曲生成对抗网络的无监督特征学习(Unsupervised representation learning with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks.)(DCGAN)
[31] Gregor, Karol, et al. DRAW:一个用于图像生成的循环神经网络(DRAW: A recurrent neural network for image generation.) (值得注意的 VAE,杰出的工作)
[32] Oord, Aaron van den, Nal Kalchbrenner, and Koray Kavukcuoglu. 像素循环神经网络(Pixel recurrent neural networks.)(像素 RNN)
[33] Oord, Aaron van den, et al. 使用像素 CNN 解码器有条件地生成图像(Conditional image generation with PixelCNN decoders.) (像素 CNN)
2.4 RNN/序列到序列模型
[34] Graves, Alex. 带有循环神经网络的生成序列(Generating sequences with recurrent neural networks.)(LSTM, 非常好的生成结果,展示了 RNN 的力量)
[35] Cho, Kyunghyun, et al. 使用 RNN 编码器-解码器学习词组表征用于统计机器翻译(Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation.) (第一个序列到序列论文)
[36] Sutskever, Ilya, Oriol Vinyals, and Quoc V. Le. 运用神经网路的序列到序列学习(Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks.」)(杰出的工作)
[37] Bahdanau, Dzmitry, KyungHyun Cho, and Yoshua Bengio. 通过共同学习来匹配和翻译神经机器翻译(Neural Machine Translation by Jointly Learning to Align and Translate.)
[38] Vinyals, Oriol, and Quoc Le. 一个神经对话模型(A neural conversational model.)(聊天机器人上的序列到序列)
2.5 神经图灵机
[39] Graves, Alex, Greg Wayne, and Ivo Danihelka. 神经图灵机器(Neural turing machines.)arXiv preprint arXiv:1410.5401 (2014). (未来计算机的基本原型)
[40] Zaremba, Wojciech, and Ilya Sutskever. 强化学习神经图灵机(Reinforcement learning neural Turing machines.)
[41] Weston, Jason, Sumit Chopra, and Antoine Bordes. 记忆网络(Memory networks.)
[42] Sukhbaatar, Sainbayar, Jason Weston, and Rob Fergus. 端到端记忆网络(End-to-end memory networks.)
[43] Vinyals, Oriol, Meire Fortunato, and Navdeep Jaitly. 指示器网络(Pointer networks.)
[44] Graves, Alex, et al. 使用带有动力外部内存的神经网络的混合计算(Hybrid computing using a neural network with dynamic external memory.)(里程碑,结合上述论文的思想)
2.6 深度强化学习
[45] Mnih, Volodymyr, et al. 使用深度强化学习玩 atari 游戏(Playing atari with deep reinforcement learning.) (第一篇以深度强化学习命名的论文)
[46] Mnih, Volodymyr, et al. 通过深度强化学习达到人类水准的控制(Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning.) (里程碑)
[47] Wang, Ziyu, Nando de Freitas, and Marc Lanctot. 用于深度强化学习的决斗网络架构(Dueling network architectures for deep reinforcement learning.) (ICLR 最佳论文,伟大的想法 )
[48] Mnih, Volodymyr, et al. 用于深度强化学习的异步方法(Asynchronous methods for deep reinforcement learning.) (当前最先进的方法)
[49] Lillicrap, Timothy P., et al. 运用深度强化学习进行持续控制(Continuous control with deep reinforcement learning.) (DDPG)
[50] Gu, Shixiang, et al. 带有模型加速的持续深层 Q-学习(Continuous Deep Q-Learning with Model-based Acceleration.)
[51] Schulman, John, et al. 信赖域策略优化(Trust region policy optimization.) (TRPO)
[52] Silver, David, et al. 使用深度神经网络和树搜索掌握围棋游戏(Mastering the game of Go with deep neural networks and tree search.) (阿尔法狗)
2.7 深度迁移学习/终身学习/尤其对于 RL
[53] Bengio, Yoshua. 表征无监督和迁移学习的深度学习(Deep Learning of Representations for Unsupervised and Transfer Learning.) (一个教程)
[54] Silver, Daniel L., Qiang Yang, and Lianghao Li. 终身机器学习系统:超越学习算法(Lifelong Machine Learning Systems: Beyond Learning Algorithms.) (一个关于终生学习的简要讨论)
[55] Hinton, Geoffrey, Oriol Vinyals, and Jeff Dean. 提取神经网络中的知识(Distilling the knowledge in a neural network.) (教父的工作)
[56] Rusu, Andrei A., et al. 策略提取(Policy distillation.) (RL 领域)
[57] Parisotto, Emilio, Jimmy Lei Ba, and Ruslan Salakhutdinov. 演员模仿:深度多任务和迁移强化学习(Actor-mimic: Deep multitask and transfer reinforcement learning.) (RL 领域)
[58] Rusu, Andrei A., et al. 渐进神经网络(Progressive neural networks.)(杰出的工作,一项全新的工作)
2.8 一次性深度学习
[59] Lake, Brenden M., Ruslan Salakhutdinov, and Joshua B. Tenenbaum. 通过概率程序归纳达到人类水准的概念学习(Human-level concept learning through probabilistic program induction.)(不是深度学习,但是值得阅读)
[60] Koch, Gregory, Richard Zemel, and Ruslan Salakhutdinov. 用于一次图像识别的孪生神经网络(Siamese Neural Networks for One-shot Image Recognition.)
[61] Santoro, Adam, et al. 用记忆增强神经网络进行一次性学习(One-shot Learning with Memory-Augmented Neural Networks ) (一个一次性学习的基本步骤)
[62] Vinyals, Oriol, et al. 用于一次性学习的匹配网络(Matching Networks for One Shot Learning.)
[63] Hariharan, Bharath, and Ross Girshick. 少量视觉物体识别(Low-shot visual object recognition.)(走向大数据的一步)
3 应用
3.1 NLP(自然语言处理)
[1] Antoine Bordes, et al. 开放文本语义分析的词和意义表征的联合学习(Joint Learning of Words and Meaning Representations for Open-Text Semantic Parsing.)
[2] Mikolov, et al. 词和短语及其组合性的分布式表征(Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality.) (word2vec)
[3] Sutskever, et al. 运用神经网络的序列到序列学习(Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks.)
[4] Ankit Kumar, et al. 问我一切:动态记忆网络用于自然语言处理(Ask Me Anything: Dynamic Memory Networks for Natural Language Processing.)
[5] Yoon Kim, et al. 角色意识的神经语言模型(Character-Aware Neural Language Models.)
[6] Jason Weston, et al. 走向人工智能-完成问题回答:一组前提玩具任务(Towards AI-Complete Question Answering: A Set of Prerequisite Toy Tasks.) (bAbI 任务)
[7] Karl Moritz Hermann, et al. 教机器阅读和理解(Teaching Machines to Read and Comprehend.)(CNN/每日邮件完形风格问题)
[8] Alexis Conneau, et al. 非常深度卷曲网络用于自然语言处理(Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Natural Language Processing.) (在文本分类中当前最好的)
[9] Armand Joulin, et al. 诡计包用于有效文本分类(Bag of Tricks for Efficient Text Classification.)(比最好的差一点,但快很多)
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)