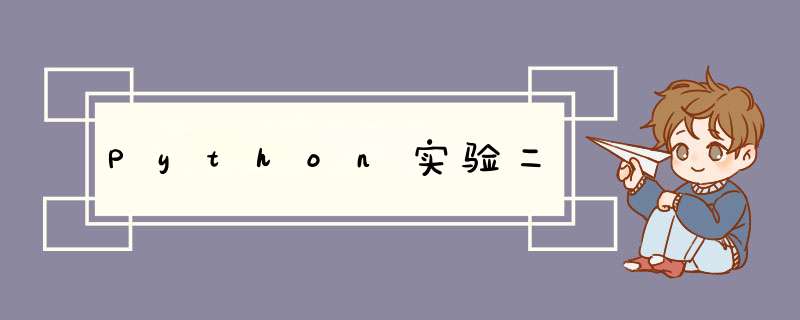
'''1. 问题描述: 编写关于学生信息的类,实例属性包括:学号、姓名、性别,班级、
n 门课程成绩,要求:
1) 利用文件读取,创建一个包含 n 个学生的班级;
文件存储格式以空格分隔例如: 202001 李四 1 班 高数:89 英语:28 计算机:77
2) n 门课程成绩利用字典存储,支持成绩录入、修改与删除;
3) 求解每个学生的 n 门成绩的平均值,及其平均值排名。并按照成绩平均成绩
排名正序输出:学号、姓名、性别、n 门课程成绩,n 门课程平均值,排名。'''
import re
class student:
def __init__(self, ID='', NAME='', GENDER='', CLASS='', GRADES=dict()):
self.ID = ID
self.NAME = NAME
self.GENDER = GENDER
self.CLASS = CLASS
self.GRADES = GRADES
@classmethod
def create_class_from_file(self, file_name):
reclass = [] # 返回的对象数组
# 读取文件
with open(file_name, encoding='utf8') as file:
lines = file.readlines()
# 逐行(对象)遍历
for line in lines:
line = line.strip('n')#strip() 方法用于移除字符串头尾指定的字符(默认为空格或换行符)或字符序列。
items = line.split(' ') # 分割出属性,空格进行分割
# 初始化各属性
ID = 'None'
NAME = 'None'
GENDER = 'None'
CLASS = 'None'
GRADES = {}
def not_set(attribute):
if attribute == 'None':
return True
else:
print("属性", attribute, "在", line, "中被重复设置,请检查是否出错")
return False
for i in items:
# 成绩
if ':' in i:
item = i.split(':')
GRADES[item[0]] = item[1]
elif i in ['男', '女'] and not_set(GENDER):
GENDER = i
# 学号(纯数字)
elif re.search('^[d]+$', i) and not_set(ID):
ID = i
# 班级(数字+班)
elif re.search('^[d]+[班]$', i) and not_set(CLASS):
CLASS = i
elif not_set(NAME):
NAME = i
reclass.append(student(ID, NAME, GENDER, CLASS, GRADES))
return reclass
def add_grades(self, dic):
self.GRADES.update(dic)
print('成绩导入')
def modify_grades(self, key, value):
if key in self.GRADES.keys():
self.GRADES[key] = value
print('修改', self.NAME, '的', key, '为', value)
else:
self.GRADES[key] = value
print('未在', self.NAME, '中找到科目', key, ',已添加为:', value)
def delete_grades(self, key):
if key in self.GRADES.keys():
print('删除:', key)
self.GRADES.pop(key)
else:
print('未在', self.NAME, '中找到科目', key)
def average_grades(self):
scores = self.GRADES.values()
sum = 0
for i in scores:
sum += int(i)
average = sum / len(scores)
return average
@classmethod#类方法,不需要实例化,直接通过类名.方法名进行调用
def sort(self, students):
stus = sorted(students, key=lambda x: x.average_grades(), reverse=True)
n = 1
for i in stus:
print(i.ID, i.NAME, i.GENDER, i.GRADES, i.average_grades(), n)
n += 1
alist = student.create_class_from_file('1班.txt')
for i in alist:
print(i.ID, i.NAME, i.GENDER, i.CLASS, i.GRADES)
plgrades = {"线代": 98, "大物": 100}
alist[0].add_grades(plgrades)
print(alist[0].GRADES)
alist[0].modify_grades("线代", 90)
print(alist[0].GRADES)
alist[0].delete_grades('线代')
print(alist[0].GRADES)
student.sort(alist)
第二题
'''2. 编程设计一个雇员基类 Employee,包括姓名,编号,月薪三个实例属性,月薪计算
pay()和信息显示 show()两个函数成员;派生两个子类 Manager 类和 Salesman 类,
重载相应的 2 个函数成员。
要求:根据以上描述设计类,并在主函数创建两个子类的实例化对象,分别调用其成员
方法。'''
class Employee:
def __init__(self,name,number,salary):#构造函数必须是__init__()命名
self.name=name
self.number=number
self.salary=salary
def pay(self):
print('Employee月薪是',self.salary)
def show(self):
print('Employee的名字是',self.name)
print('Employee编号是',self.number)
class Manager(Employee):
def pay(self):
print('Manager月薪是',self.salary)
def show(self):
print('Manager的名字是',self.name)
print('Manager编号是',self.number)
class Salesman(Employee):
def pay(self):
print('Salesman月薪是',self.salary)
def show(self):
print('Salesman的名字是',self.name)
print('Salesman编号是',self.number)
ligen=Employee('li',10,4000)
ligen.show()
ligen.pay()
xwh=Manager('xwh','2020',3500)
xwh.show()
xwh.pay()
mrj=Salesman('mrj',9,2000)
mrj.show()
mrj.pay()
第三题
'''3. 编程设计一个基类汽车类 Vehicle,包含最大速度 MaxSpeed,weight 两个实例私
有属性;设计一个派生子类自行车(Bicycle)类,增加 1 个实例私有属性高度(height)
和 1 个成员函数 SetMaxSpeed 实现给父类的实例属性 MaxSpeed 的赋值。
要求:
1) 根据以上描述设计类,并在主函数中创建子类的实例化对象,并设置对象的
MaxSpeed 值。
2) 利用 property 将 height 设定为可读、可修改的属性。'''
class Vehicle:
MaxSpeed=200
weight=150
def show(self):
print('汽车的最大速度为',self.MaxSpeed)
print('汽车的重量为',self.weight)
class Bicycle(Vehicle):
def __init__(self,height):
self.__height = height
def set_MaxSpeed(self,Maxspeed):
self.MaxSpeed=Maxspeed
def set_weight(self,weight):
self.weight=weight
def __get(self):
return self.__height
def __set(self,h):
self.__height=h
def show(self):
print('自行车的高度为',self.__height)
print('自行车的最大速度为',self.MaxSpeed)
print('自行车的重量为',self.weight)
height = property(__get,__set)#使用property时,必须用__get,__set,以及__height
car=Vehicle()
car.show()
bike=Bicycle(20)
bike.set_weight(10)
bike.set_MaxSpeed(50)
bike.show()
print('****高度修改后的为****')
bike.height=3
bike.show()
第四题
'''4. 编程设计一个队列类 Myqueue,主要的类成员包括: 3 个数据成员(队列的最大
长度 size,队列所有数据 data,队列的元素个数 current)和 6 个成员方法如下:
1) 初始化 :设置队列为空;
2) 判断队列为空:若为空,则返回 TRUE,否则返回 FALSE.
3) 判断队列为满:若为满,则返回 TRUE,否则返回 FALSE.
4) 取队头元素:取出队头元素;
条件:队列不空。
否则,应能明确给出标识,以便程序的处理.
5) 入队:将元素入队,即放到队列的尾部
6) 出队:删除当前队头的元素
要求:根据以上描述设计类,并在主函数中创建类的实例化对象,构建一个长度为 N
的队列,分别调用上述成员方法。'''
#队列;先进先出
class Myqueue(object):
def __init__(self): #定义一个空队列
self.queue = []
def in_queue(self,element): #1个元素入队列
self.queue.append(element)
print('元素%s入队列成功!'%element)
def many_in_queue(self,*args): #多个元素入队列
self.queue.extend(args)
def out_queue(self): #出队列
if not self.queue == []: #队列不为空时,d出第一个元素
out_element = self.queue.pop(0)
print('元素%s出队列成功!'%out_element)
else:
print('队列为空,无法出队列!') #队列为空时报错
def head(self): #队列首元素
if not self.queue == []: #队列不为空
print('队列首元素为%s'%self.queue[0])
else:
print('队列为空,无队列首元素!')
def tail(self): #队列尾元素
if not self.queue == []: #队列不为空
print('队列尾元素为%s'%self.queue[-1])
else:
print('队列为空,无队列尾元素!') #对列为空时报错
def length(self): #队列长度
print('队列的长度为%s'%len(self.queue))
def show(self): #显示队列
print('队列为:')
for i in self.queue:
print(i,',',end='')
print()
def is_empty(self): #判断队列是否为空
if len(self.queue) == 0:
print('队列为空!')
else:
print('队列不为空!')
queue1=Myqueue()
queue1.is_empty()
queue1.in_queue(1)
queue1.is_empty()
queue1.many_in_queue(1,3,4,5,7,8)
queue1.show()
queue1.head()
queue1.tail()
queue1.length()
queue1.out_queue()
queue1.is_empty()
第五题
#5. 问题描述:编写程序,生成多个字符串,将字符串写入文件,同时读取当前文件,
#并输出统计字符串的个数。
s = 'hello thank you thank you very much'
# 写将字符串写入
f = open(r'F:'Monday.txt','w')
f.write(s)
f.close
# 导入模块
import collections
import re
def fun():
with open(r'F:'Monday.txt', 'r') as fp:
content = re.split('[,. ]', fp.read())
print(content)
b = collections.Counter(content)#计算可迭代序列中各个元素的数量
print(b)
with open(r'F:'word2.txt', 'w') as result_file:
for key, value in b.items():
result_file.write(key + ':' + str(value) + 'n')
# 字符串替换
list1 = s.replace(',', ' ')
list2 = list1.replace('.', ' ')
print(list2)
# 字符串截取
list3 = list2.split(' ')
print(list3)
# 创建空字典
d = {}
# 遍历列表
for i in list3:
ss = d.get(i)
if ss == None:
d[i] = 1
else:
d[i] += 1
print(d)
# 将字典的值变为列表进行排序
d1 = sorted(d.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
print(d1)
fun()
第六题
#假设有一个英文文本文件,编写程序读取其内容,并将其中的大写字母变为小写字母,小写字母变为大写字母
f = open(r'F:'demo.txt','r')
s=f.readlines()
f.close()
r=[i.swapcase() for i in s] #swapcase()将大小写转换
f=open(r'F:'demo.txt','w+')
f.writelines(r)
f.seek(0)#将指针移动到指定字节的位置
ss=f.read()
f.close()
print('转换结果为:',ss)
第七题
#7. 编写多进程的程序,程序先输出主进程的 ID,然后创建一个子进程,子进程中输出自己的 ID。
import threading
import time
def fun1():
print('主进程ID:12345')
time.sleep(3)
def fun2():
print('子进程ID:67890')
t1=threading.Thread(target=fun1())
t1.start()
t2=threading.Thread(target=fun2())
t2.start()
第八题
def ysf(sum,bsit,distance,survive):#sum总的人数,bsit报数开始的位置,distance报数的间距,survive存活多少人时停止
people={}
for i in range(1,sum+1):
people[i]=1
t=bsit
j=sum
check=0
while t<=sum+1:
if t==sum+1:
t=1
elif j==survive:
break
else:
if people[t]==0:
t+=1
continue
else:
check+=1
if check==distance:
people[t]=0
check=0
print("{}号淘汰".format(t))
#print(people)
j-=1
else:
t+=1
for k in range(1,sum+1):
if people[k]==1:
print(k,"号存活")
x=int(input('请输入约瑟夫环人数'))
ysf(x,1,3,1)
第九题
'''9. 编写程序以检查用户输入的密码的有效性。
检查密码的标准为:
1. [a-z]之间至少有 1 个字母
2. [0-9]之间至少有 1 个数字
1. [A-Z]之间至少有一个字母
3. [$#@]中至少有 1 个字符
4.最短交易密码长度:6
5.交易密码的最大长度:12
程序接受一系列逗号分隔的密码,进行检查。再输出符合条件的密码,每个密码用逗
号分隔。
例如:程序的输入:
abcdEF12#@,ccword12
程序的输出:
abcdEF12#@'''
import re
import string
def Check_Password(pwd):
if len(pwd) < 6 or len(pwd) > 12:
return "密码长度不符合6到12位"
flag = [False] * 4#flag函数起到标记标识的作用,有四个标记
for ch in pwd:
if ch in string.ascii_lowercase: # 检查是否有小写
flag[0] = True
if ch in string.ascii_uppercase: # 检查是否有大写
flag[1] = True
if ch in string.digits: # 检查是否包含数字
flag[2] = True
if ch in '$#@':#检查是否包含特殊字符串
flag[3] = True
if flag.count(True) == 4:#检查四个标记是否都正确
return pwd
return "格式不对"
str1 = input("请输入密码,逗号分隔")
alist = str1.split(",")
for pwd in alist:
print(Check_Password(pwd))
第十题
value = []
print('请输入逗号分隔的4位二进制数:')
items = [x for x in input().split(',')]
for p in items:
intp = int(p, 2)
# print(intp)
if not intp % 5:
value.append(p)
print(','.join(value),'可被5整除')#join函数连接字符串数组
第十一题
#11. 在一个坐标系中,绘出两个函数的图形,分别 y=sin(x)和 y=cos(x),x 坐标取值范围为(0, 2ᅲ)
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6), dpi=80)#生成一张画板
x = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 256, endpoint=True)#创建自变量数组
C, S = np.cos(x), np.sin(x)#计算正弦函数以及余弦函数的数值
# 设置线的颜色,粗细,和线型
plt.plot(x, C, color="blue", linewidth=2.5, linestyle="-", label=r'$sin(x)$')
plt.plot(x, S, color="red", linewidth=2.5, linestyle="-", label=r'$cos(x)$')
# 如果觉得线条离边界太近了,可以加大距离
plt.xlim(x.min() * 1.2, x.max() * 1.2)
plt.ylim(C.min() * 1.2, C.max() * 1.2)
# 当前的刻度并不清晰,需要重新设定,并加上更直观的标签
plt.xticks([ 0,2* np.pi],
[r'$', r'$+2pi$'])
plt.yticks([-1, 0, 1],
[r'$-1$', r'$', r'$'])
# 添加图例
plt.legend()
plt.show()
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)