IntroducTIonThis document describes how to use the 1-Wire Public Domain (PD) Kit. The kit was built to assist any developer creating an application that uses Maxim's 1-Wire devices. The kit is also a learning tool to understand how to communicate to the 1-Wire network.
This article explains how to combine the files in the kit to form an application. It also shows how to build custom applications for a different OS platform, even if one is not already supported.
The source code in the 1-Wire PD kit was written in C. This language was selected because it is one of the most common programming languages and is highly portable to different operating systems. Application note 155, "1-Wire® Software Resource Guide Device Description," describes the 1-Wire PD kit and other software development kits that are available.
API Function GroupingThe software functions in the 1-Wire PD kit API are grouped together (usually into separate files) according to their intended purpose.
- The Session group acquires and releases exclusive use of the 1-Wire so that no other application can interfere with communication.
- The Link group is a set of primitive 1-Wire communication functions, which include reset, reading/writing bits, EPROM programming pulse, and power delivery. These Link functions are platform-dependent.
- The Network function group performs device discovery and selection operations. Each 1-Wire device has a 1-Wire network address for individual selection.
- The Transport group performs block communication and primitive read/write memory functions, which include packet read/write functions to 1-Wire devices.
- The File group contains memory-level functions that use the 1-Wire File Structure (see application note 114, "1-Wire File Structure"). The File group can be used on 1-Wire devices with more than one page of memory.
- The Device group uses the above functional groups to perform specific operations on 1-Wire devices. These operations include SHA operations, temperature readings, voltage readings, and setting switch states.
There are three standard methods to build the lowest level of the API for a particular platform. The first method is called "general" and the second is called "userial." The general build method requires the developer to implement the primitive link-level 1-Wire communication functions. See application note 126, "1-Wire Communication Through Software," for more details. The userial build method is strictly for the RS-232 serial port and assumes that the developer will utilize Maxim's DS2480B, the Universal Serial 1-Wire Line Driver Master. The only software functionality to implement for a userial platform build is the serial-port read/write primitives. See application note 192, "Using the DS2480B Serial 1-Wire Line Driver," for more details. Maxim sells several DS2480B-based PC serial adapters, such as the DS9097U-009, DS9097U-S09, DS9097U-E25, DS1411-009, and DS1411-S09.
A third, "other" implementation category provides the standard 1-Wire PD kit basic API, but can diverge in API implementation by taking advantage of particular system or adapter features. For example, implementations of the API using a 1-Wire USB adapter, such as the DS9490R, require this category to take advantage of the USB port and special features built into the adapter.
The Figure 1 flow-chart steps through the decisions that ensure optimal use of the kit.
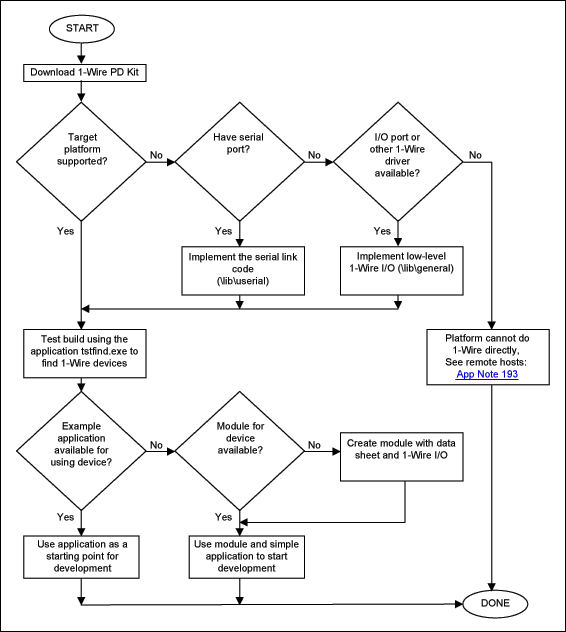
Figure 1. Usage flowchart for the 1-Wire PD kit.
How to Create an ApplicationThe kit files are organized into several subdirectories.
- The files in the \apps directory can be used with the files in the \common directory to form an application basis for any port or platform.
- The files in the lib\general and the lib\userial are the two sets of portable source files discussed earlier.
- The last task for putting the application together is the Link file, which can be found in either \lib\userial\link or \lib\general\link. If the link file does not exist for the target platform, then you must complete the source code template files (for example, the TODO.C file for "userial" builds) provided with the kit. These link files have functions for your port and platform that need to be filled in correctly to get the 1-Wire PD kit working. Figure 2 illustrates gathering all the files together with an existing Link file.
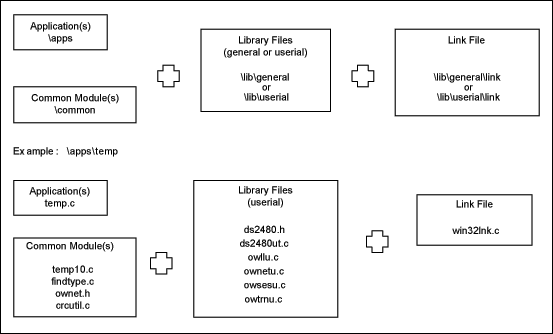
Figure 2. Files needed to construct an application.
Table 1 shows the various platforms currently supported by the kit. The platforms can be downloaded from the 1-Wire Public Domain kit main page.
Table 1. Software Platforms Supported by the 1-Wire PD kit
COM
LPT multiport multiw32vc
COM
LPT multiport multiw64vc
1-Wire is a registered trademark of Maxim Integrated Products, Inc.
iButton is a registered trademark of Maxim Integrated Products, Inc.
Keil Software is a registered trademark of Keil Software, Inc.
Linux is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds.
Mac OS is a registered trademark of Apple Inc.
Win32 is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)