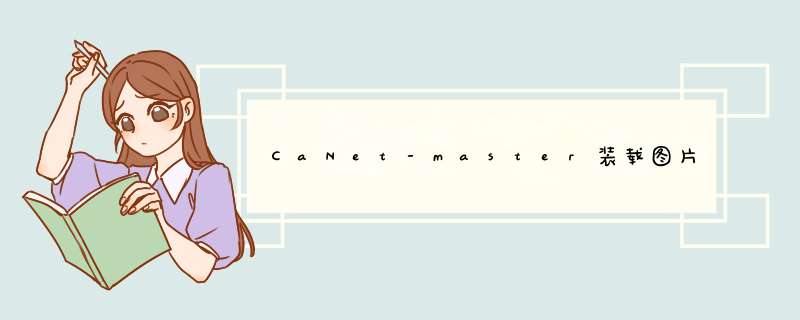
训练需要support set原图+mask,query set原图,使用query集计算loss更新参数。
support set和query set的cls一样,但是取的不同的图
query_name = self.new_exist_class_list[index][0]
sample_class = self.new_exist_class_list[index][1] # random sample a class in this img
# return class's mask_list
support_img_list = self.binary_pair_list[sample_class] # all img that contain the sample_class
pred = model(query_rgb, support_rgb, support_mask, history_mask)
loss = loss_calc_v1(pred, query_mask, 0)
一、Dataset、Dataloader数据处理 PIL读入之后对象中w, h = img.size,转为numpy数组后变为:h,w,c(通道是RGB),转为Tensor后变为:c,h,w,最后如果要使用cv2保存图像需要转为:h,w,c 1.1 数据集文件夹:
1.2 Dataset和Dataloader:首先自定义Dataset类重写__getitem__方法:index对应单张图片序号,batch_size不同也可能取到不同的类: 1 w a y − 1 s h o t \color{red}{1 way-1shot} 1way−1shot
# loading data
# trainset
dataset = Dataset_train(data_dir=data_dir, fold=options.fold, input_size=input_size, normalize_mean=IMG_MEAN,
normalize_std=IMG_STD,prob=options.prob)
trainloader = data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=4)
# ipdb.set_trace()
# valset
# this only a quick val dataset where all images are 321*321.
valset = Dataset_val(data_dir=data_dir, fold=options.fold, input_size=input_size, normalize_mean=IMG_MEAN,
normalize_std=IMG_STD)
valloader = data.DataLoader(valset, batch_size=options.bs_val, shuffle=False, num_workers=4,
drop_last=False)
index对应单张图片序号
每个split文件夹的图片及类别数量如下:
| 文件夹 | 图片+类别 数量 |
|---|---|
| split0_train.txt | 2286 |
| split1_train.txt | 3425 |
| split2_train.txt | 5883 |
| split3_train.txt | 2086 |
由于我是设置fold 0作为测试集:
parser.add_argument('-fold', type=int, help='fold', default=0)
所以new_exist_class_list
[
0
]
\color{red}{[0]}
[0]得到的是除split0_train.txt文件之外的三个文件夹列表
训
练
集
\color{red}{训练集}
训练集new_exist_class_list中训练集某张图片名称,**new_exist_class_list
[
1
]
\color{red}{[1]}
[1]得到这张训练图片所属类别:
**binary_pair_list[sample_class]**从1.txt文件中得到此类别的所有图片名称的列表。
判断list中与query_name不同,来得到支撑集图片名称:
while True:
support_name = support_img_list[random.randint(0, len(support_img_list) - 1)] # [0, l-1]
if support_name != query_name:
break
Binary_map_aug文件夹中读取到了support和query的图片名称在这里插入代码片
CaNet/CaNet-master/dataset/dir/VOCdevkit/VOC2012/Binary_map_aug/train/
由于pytorch的顺序是
(
b
a
t
c
h
,
c
,
h
,
w
)
\color{red}{(batch,c,h,w)}
(batch,c,h,w),所以需要进行PIL类型到numpy类型转换,tensorflow,numpy的顺序是(batch,h,w,c):
PIL可以完美配合plt,但是如果使用PIL和imread显示的话要将RGB转换为BGR。
support_rgb = self.normalize(
self.ToTensor(
scale_transform_rgb(
self.flip(flip_flag,
# PIL format
Image.open(os.path.join(self.data_dir, 'JPEGImages', support_name + '.jpg'))
))))
-
c
v
2.
i
m
r
e
a
d
(
)
\color{red}{cv2.imread()}
cv2.imread()得到的img数据类型是np.array()类型。
B G R ( 默 认 ) \color{red}{BGR(默认)} BGR(默认)
- 通过Image.open(path)读入的图片为Image对象,不是普通的数组。
w , h = i m g . s i z e \color{red}{w, h = img.size} w,h=img.size、 R G B ( 默 认 ) \color{red}{RGB(默认)} RGB(默认)
将 P I L \color{red}{PIL} PIL类型转化成numpy类型之后: H ∗ W ∗ C \color{red}{H*W*C} H∗W∗C -
p
l
t
\color{red}{plt}
plt。
matplotlib.pyplot.imshow()和matplotlib.pyplot.show()正好可以对应PIL对象读入的RGB,示例如下:
# 2. cover show
def show_mask_in_img2(imgfile, maskfile, trueMaskfile):
image1 = Image.open(imgfile)
image2 = Image.open(maskfile)
image3 = Image.open(trueMaskfile)
plt.figure()
plt.subplot(221)
plt.imshow(image1)
plt.subplot(222)
plt.imshow(image2)
plt.subplot(223)
plt.imshow(image1)
plt.imshow(image2, alpha=0.5)
plt.subplot(224)
plt.imshow(image3)
plt.show()
在用plt.imshow和cv2.imshow显示同一幅图时可能会出现颜色差别很大的现象。 这是因为:
opencv的接口使用BGR,而matplotlib.pyplot 则是RGB模式
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
img = cv2.imread('lena_std.tif')
b,g,r = cv2.split(img)
img2 = cv2.merge([r,g,b])
plt.subplot(121);plt.imshow(img)
plt.subplot(122);plt.imshow(img2)
plt.show()
cv2.imshow('bgr image',img)
cv2.imshow('rgb image',img2)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
程序运行结果如下:
Matplotlib显示结果
OpenCV显示结果
参考:Extracting a region from an image using slicing in Python, OpenCV
Image.open加载图片的代码示例如下:
# Load Image
img_fn = os.path.join(self.input_path, filenames)
img = Image.open(img_fn) # RGB(默认)
# img.show()
# resize/crop if needed:[128*128*3]
if self.input_size != 0:
height = width = self.input_size
img = img.resize((height, width), Image.BILINEAR)
# 将PIL类型转化成numpy类型
img = np.array(img).uint8() # H*W*C
Ps:transforms.Resize()的简单用法
而一般输入深度网络的特征图长宽是相等的,就不能采取等比例缩放的方式了,需要同时指定长宽:
transforms.Resize([h, w])
例如transforms.Resize([224, 224])就能将输入图片转化成224×224的输入特征图。
这样虽然会改变图片的长宽比,但是本身并没有发生裁切,仍可以通过resize方法返回原来的形状:
from PIL import Image
from torchvision import transforms
img = Image.open('1.jpg')
w, h = img.size
resize = transforms.Resize([224,244])
img = resize(img)
img.save('2.jpg')
resize2 = transforms.Resize([h, w])
img = resize2(img)
img.save('3.jpg')
需要注意的一点是PILImage对象size属性返回的是w, h,而resize的参数顺序是h, w。
注:对于Image.open()函数默认彩色图像读取通道的顺序为RGB,而cv2.imread()读取通道的顺序为BGR。
当 图 像 格 式 为 R G B A 时 \color{red}{当图像格式为RGBA时} 当图像格式为RGBA时,Image.open(‘—.jpg’)读取的格式为RGBA(其中A表示图像的alpha通道,即RGBA共四个通道),而cv2.imread(’—.jpg’)读取的格式是BGR,只有三个通道。
通过使用cv2.split(img)可得到cv2.imread()读取的图片img的BGR通道值。
即使图片是RGBA四通道,cv2.imread()方法仍然读取的是BGR三通道。
resize的尺寸(根据random()函数来看是取不到1.5的):
# uniform(1 , 6)
# output: 3.001161523486847
scaled_size = int(random.uniform(1, 1.5)*input_size)
Ps:Python 中的 random.uniform( ) 函数
- x – 随机数的最小值,包含该值。
- y – 随机数的最大值,不包含该值。
- 返回一个浮点数
实例
# _*_ coding: utf-8 _*_
import random
print("uniform(1 , 6) 的随机返回值为 : ", random.uniform(1 , 6))
print("uniform(10, 16) 的随机返回值为 : ", random.uniform(10, 16))
# 输出:
# uniform(1 , 6) 的随机返回值为 : 3.001161523486847
# uniform(10, 16) 的随机返回值为 : 13.70906147017741
flip水平翻转random()概率
output: 0 <= n < 1.0
flip_flag = random.random()
Ps:CaNet-master中代码,当random出的值>0.5的时候才会进行水平翻转:
def flip(self, flag, img):
if flag > 0.5:
return F.hflip(img)
else:
return img
最后调用ToTensor函数从 H ∗ W ∗ C \color{red}{H*W*C} H∗W∗C转为 C ∗ H ∗ W \color{red}{C*H*W} C∗H∗W:
self.ToTensor = torchvision.transforms.ToTensor()
save_pred_every = len(trainloader)
1.23 DataLoader定义batch_size装载图片 C ∗ H ∗ W \color{red}{C*H*W} C∗H∗W为 B ∗ C ∗ H ∗ W \color{red}{B*C*H*W} B∗C∗H∗W下面的save_pred_every = len(trainloader)其实是11394/4=2848.5之后没有抛弃得到的2849个batch_size
dataset = Dataset_train(data_dir=data_dir, fold=options.fold, input_size=input_size, normalize_mean=IMG_MEAN,
normalize_std=IMG_STD,prob=options.prob)
trainloader = data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=4)
# ipdb.set_trace()
# valset
# this only a quick val dataset where all images are 321*321.
valset = Dataset_val(data_dir=data_dir, fold=options.fold, input_size=input_size, normalize_mean=IMG_MEAN,
normalize_std=IMG_STD)
valloader = data.DataLoader(valset, batch_size=options.bs_val, shuffle=False, num_workers=4,
drop_last=False)
附:CaNet-master Dataset类__getitem__方法完整代码:
def __getitem__(self, index):
# new_exist_class_list.append([img_name, class],...)
# give an query index,sample a target class first
query_name = self.new_exist_class_list[index][0]
sample_class = self.new_exist_class_list[index][1] # random sample a class in this img
# return class's mask_list
support_img_list = self.binary_pair_list[sample_class] # all img that contain the sample_class
# random sample a img_class's data, ensure different from query_name
while True:
support_name = support_img_list[random.randint(0, len(support_img_list) - 1)] # [0, l-1]
if support_name != query_name:
break
# input_size=[321, 321]
input_size = self.input_size[0]
# random scale and crop for support
# uniform(1 , 6)
# output: 3.001161523486847
scaled_size = int(random.uniform(1, 1.5)*input_size)
# interpolation (int, optional): Desired interpolation enum defined by `filters`_.
# Default is ``PIL.Image.BILINEAR``.
# If input is Tensor, only ``PIL.Image.NEAREST``, ``PIL.Image.BILINEAR``and ``PIL.Image.BICUBIC`` are supported.
scale_transform_mask = torchvision.transforms.Resize([scaled_size, scaled_size], interpolation=Image.NEAREST)
scale_transform_rgb = torchvision.transforms.Resize([scaled_size, scaled_size], interpolation=Image.BILINEAR)
# output: 0 <= n < 1.0
flip_flag = random.random()
support_rgb = self.normalize(
self.ToTensor(
scale_transform_rgb(
self.flip(flip_flag,
# PIL format
Image.open(os.path.join(self.data_dir, 'JPEGImages', support_name + '.jpg'))
))))
support_mask = self.ToTensor(
scale_transform_mask(
self.flip(flip_flag,
Image.open(
os.path.join(self.data_dir, 'Binary_map_aug', 'train', str(sample_class),
support_name + '.png')))))
margin_h = random.randint(0, scaled_size - input_size)
margin_w = random.randint(0, scaled_size - input_size)
# 3 * h * w, size_h_w
support_rgb = support_rgb[:, margin_h:margin_h + input_size, margin_w:margin_w + input_size]
support_mask = support_mask[:, margin_h:margin_h + input_size, margin_w:margin_w + input_size]
# random scale and crop for query
scaled_size = input_size
scale_transform_mask = torchvision.transforms.Resize([scaled_size, scaled_size], interpolation=Image.NEAREST)
scale_transform_rgb = torchvision.transforms.Resize([scaled_size, scaled_size], interpolation=Image.BILINEAR)
# query imgs don't flip
flip_flag = 0
query_rgb = self.normalize(
self.ToTensor(
scale_transform_rgb(
self.flip(flip_flag,
Image.open(
os.path.join(self.data_dir, 'JPEGImages', query_name + '.jpg'))))))
query_mask = self.ToTensor(
scale_transform_mask(
self.flip(flip_flag,
Image.open(
os.path.join(self.data_dir, 'Binary_map_aug', 'train', str(sample_class),
query_name + '.png')))))
margin_h = random.randint(0, scaled_size - input_size)
margin_w = random.randint(0, scaled_size - input_size)
# ipdb.set_trace()
query_rgb = query_rgb[:, margin_h:margin_h + input_size, margin_w:margin_w + input_size]
query_mask = query_mask[:, margin_h:margin_h + input_size, margin_w:margin_w + input_size]
if self.history_mask_list[index] is None:
history_mask = torch.zeros(2,41,41).fill_(0.0)
else:
if random.random() > self.prob:
history_mask = self.history_mask_list[index]
else:
history_mask = torch.zeros(2, 41, 41).fill_(0.0)
return query_rgb, query_mask, support_rgb, support_mask, history_mask, sample_class, index
def flip(self, flag, img):
if flag > 0.5:
return F.hflip(img)
else:
return img
def __len__(self):
return len(self.new_exist_class_list)
二、网络训练
针对每一个epoch都有如下:
for epoch in range(0, num_epoch):
begin_time = time.time()
tqdm_gen = tqdm.tqdm(trainloader)
for i_iter, batch in enumerate(tqdm_gen):
query_rgb, query_mask, support_rgb, support_mask, history_mask, sample_class, index = batch
query_rgb = (query_rgb).cuda(0)
support_rgb = (support_rgb).cuda(0)
support_mask = (support_mask).cuda(0)
query_mask = (query_mask).cuda(0).long() # change formation for crossentropy use
query_mask = query_mask[:, 0, :, :] # remove the second dim,change formation for crossentropy use
history_mask=(history_mask).cuda(0)
optimizer.zero_grad()
# pred = torch.Size([4, 2, 41, 41])
pred = model(query_rgb, support_rgb, support_mask, history_mask)
# index 1 sum = 1
pred_softmax = F.softmax(pred, dim=1).data.cpu()
# update history mask
for j in range (support_mask.shape[0]):
sub_index = index[j]
dataset.history_mask_list[sub_index] = pred_softmax[j]
pred = nn.functional.interpolate(pred, size=input_size, mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)# upsample
# pred:[4, 2, 321, 321]
# query mask:[4, 321, 321]
# output: tensor(n)
loss = loss_calc_v1(pred, query_mask, 0)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# highest_iou is last epoch max iou
# tqdm_gen.set_description('e:%d loss = %.4f-:%.4f' % (
tqdm_gen.set_description('epoch:%d loss = %.4f-:%.4f' % (epoch, loss.item(), highest_iou))
# save training loss
tempory_loss += loss.item()
if i_iter % (save_pred_every - 1) == 0 and i_iter != 0: # every epoch: save
print("---------------save----------------")
loss_list.append(tempory_loss / save_pred_every)
plot_loss(checkpoint_dir, loss_list, save_pred_every)
np.savetxt(os.path.join(checkpoint_dir, 'loss_history.txt'), np.array(loss_list))
tempory_loss = 0
其中pred的tensor尺寸: p r e d = t o r c h . S i z e ( [ 4 , 2 , 41 , 41 ] ) \color{red}{pred = torch.Size([4, 2, 41, 41])} pred=torch.Size([4,2,41,41])
2.1 torch.max(input, dim) 函数pred = model(query_rgb, support_rgb, support_mask, history_mask)
- 返回值:减少一个维度,两个Tensor 索引的最大值,索引)
_, pred_label = torch.max(pred, 1)
随后pred_label维度从 [ 64 , 2 , 321 , 321 ] \color{red}{[64, 2, 321, 321]} [64,2,321,321]变为:
- pred_label: [ 64 , 321 , 321 ] \color{red}{[64, 321, 321]} [64,321,321]
- query_mask:[64, 321, 321]
在64这里是每张图的最大值下标:0/1
下面通过一个实例可以更容易理解这个函数的用法。inter_list, union_list, _, num_predict_list = get_iou_v1(query_mask, pred_label)
import torch
a = torch.tensor([[1,5,62,54], [2,6,2,6], [2,65,2,6]])
print(a)
# 输出:
tensor([[ 1, 5, 62, 54],
[ 2, 6, 2, 6],
[ 2, 65, 2, 6]])
索引每行的最大值:(在计算准确率时第一个tensor values是不需要的,所以我们只需提取第二个tensor,并将tensor格式的数据转换成array格式。
)
torch.max(a, 1)
# 输出:
torch.return_types.max(
values=tensor([62, 6, 65]),
indices=tensor([2, 3, 1]))
之后经过softmax后(index 1 sum = 1),之后尺寸变为:
p
r
e
d
s
o
f
t
m
a
x
=
T
e
n
s
o
r
:
(
4
,
2
,
41
,
41
)
\color{red}{pred_softmax=Tensor:(4,2,41,41)}
predsoftmax=Tensor:(4,2,41,41)
其中,[4, 2, 41, 41]的softmax dim=1表示每一个像素点2class概率之和为1。
(2分类:背景目标)
pred_softmax = F.softmax(pred, dim=1).data.cpu()
Ps:F.softmax()的用法
softmax的维度为1的时候,是下标为1的这个维度所有元素之和为1:
>>> import torch
>>> import torch.nn.functional as F
>>> logits = torch.rand(2,2)
>>> pred = F.softmax(logits, dim=1)
>>> logits
tensor([[0.4140, 0.4571],
[0.9392, 0.6504]])
>>> pred
tensor([[0.4892, 0.5108],
[0.5717, 0.4283]])
>>>
这个函数是用来上采样或下采样,可以给定size或者scale_factor来进行上下采样。
同时支持3D、4D、5D的张量输入。
插值算法可选:最近邻、线性、双线性等等。
CaNet-master代码使用双线性插值上采样:
pred = nn.functional.interpolate(pred, size=input_size, mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)# upsample
- pred:[4, 2, 321, 321]
- query mask:[4, 321, 321]
- output: tensor(n)
loss = loss_calc_v1(pred, query_mask, 0)
看代码是直接使用的交叉熵损失
Pytorch中CrossEntropyLoss()函数的主要是将softmax-log-NLLLoss合并到一块得到的结果。
1、Softmax后的数值都在0~1之间,所以ln之后值域是负无穷到0。
2、然后将Softmax之后的结果取log,将乘法改成加法减少计算量,同时保障函数的单调性 。
其
nn.CrossEntropyLoss()的计算公式为:
其中x是网络的输出向量,class是真实标签。
代码:
# pred:[4, 2, 321, 321]
# query mask:[4, 321, 321]
# output : tensor
def loss_calc_v1(pred, label, gpu):
label = label.long()
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss(ignore_index=255).cuda(gpu)
return criterion(pred, label)
三、验证集val Evaluation
pred = model(query_rgb, support_rgb, support_mask, history_mask)
pred_softmax = F.softmax(pred, dim=1).data.cpu()
# update history mask
for j in range(support_mask.shape[0]):
sub_index = index[j]
valset.history_mask_list[sub_index] = pred_softmax[j]
# pred:[4, 2, 321, 321]
pred = nn.functional.interpolate(pred, size=input_size, mode='bilinear',
align_corners=True) # upsample # upsample
_, pred_label = torch.max(pred, 1)
# pred_label:[64, 321, 321]
# query_mask:[64, 321, 321]
inter_list, union_list, _, num_predict_list = get_iou_v1(query_mask, pred_label)
for j in range(query_mask.shape[0]): # batch size
# fold 0 : 1-5 - 10
# fold 1 : 6-10 - 6
all_inter[sample_class[j] - (options.fold * 5 + 1)] += inter_list[j]
all_union[sample_class[j] - (options.fold * 5 + 1)] += union_list[j]
(pred_label[i] > 0)
输出布尔值的Tensor:
(pred_label[i] > 0).float()
输出0/1值的Tensor:
torch.sum((pred_label[i] > 0).float())
Tensor.item()
.item()方法返回张量元素的值。
其中sample_class经过打包之后变成:
query_rgb, query_mask, support_rgb, support_mask, history_mask, sample_class, index = batch
四、损失函数 4.1 val 4.11 在eval()阶段会使用with torch.no_grad()
而使用no_grad则设置让梯度Autograd设置为False(因为在训练中我们默认是True),这样保证了反向过程为纯粹的测试,而不变参数。
参考文档说这样避免每一个参数都要设置,解放了GPU底层的时间开销,在测试阶段统一梯度设置为False
for i_iter, batch in enumerate(valloader):
query_rgb, query_mask, support_rgb, support_mask, history_mask, sample_class, index = batch
query_rgb = (query_rgb).cuda(0)
support_rgb = (support_rgb).cuda(0)
support_mask = (support_mask).cuda(0)
query_mask = (query_mask).cuda(0).long() # change formation for crossentropy use
query_mask = query_mask[:, 0, :, :] # remove the second dim,change formation for crossentropy use
history_mask = (history_mask).cuda(0)
pred = model(query_rgb, support_rgb, support_mask, history_mask)
pred_softmax = F.softmax(pred, dim=1).data.cpu()
# update history mask
for j in range(support_mask.shape[0]):
sub_index = index[j]
valset.history_mask_list[sub_index] = pred_softmax[j]
# pred:[4, 2, 321, 321]
pred = nn.functional.interpolate(pred, size=input_size, mode='bilinear',
align_corners=True) #upsample # upsample
_, pred_label = torch.max(pred, 1)
# pred_label:[64, 321, 321]
# query_mask:[64, 321, 321]
inter_list, union_list, _, num_predict_list = get_iou_v1(query_mask, pred_label)
for j in range(query_mask.shape[0]): # batch size
# fold 0 : 1-5 - 10
# fold 1 : 6-10 - 6
all_inter[sample_class[j] - (options.fold * 5 + 1)] += inter_list[j]
all_union[sample_class[j] - (options.fold * 5 + 1)] += union_list[j]
IOU = [0] * 5
for j in range(5):
IOU[j] = all_inter[j] / all_union[j]
mean_iou = np.mean(IOU)
print('IOU:%.4f' % (mean_iou))
if mean_iou > best_iou:
best_iou = mean_iou
else:
break
for j in range(query_mask.shape[0]): # batch size
# fold 0 : 1-5 - 10
# fold 1 : 6-10 - 6
all_inter[sample_class[j] - (options.fold * 5 + 1)] += inter_list[j]
all_union[sample_class[j] - (options.fold * 5 + 1)] += union_list[j]
由于每次测试使用5cls,所以枚举5次,索引0-4,计算 I O U \color{red}{IOU} IOU和 m I O U \color{red}{mIOU} mIOU:
for j in range(5):
IOU[j] = all_inter[j] / all_union[j]
mean_iou = np.mean(IOU)
保存best_iou
print('IOU:%.4f' % (mean_iou))
if mean_iou > best_iou:
best_iou = mean_iou
else:
break
iou_list.append(best_iou)
plot_iou(checkpoint_dir, iou_list)
np.savetxt(os.path.join(checkpoint_dir, 'iou_history.txt'), np.array(iou_list))
if best_iou > highest_iou:
highest_iou = best_iou
model = model.eval()
torch.save(model.cpu().state_dict(), osp.join(checkpoint_dir, 'model', 'best' '.pth'))
model = model.train()
best_epoch = epoch
print('A better model is saved')
一般情况下,我们训练过程如下:
1、拿到数据后进行训练,在训练过程中,使用
model.train():告诉我们的网络,这个阶段是用来训练的,可以更新参数。
2、训练完成后进行预测,在预测过程中,使用
model.eval() : 告诉我们的网络,这个阶段是用来测试的,于是模型的参数在该阶段不进行更新。
其中,里面的model = model.eval()、model = model.train()
五、可视化
自己写了一个test.py函数。
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(pthfile, map_location='cpu'))
model.cuda()
- Image.open()之后对象通道数为: [ W , H ] \color{red}{[W, H]} [W,H],可以通过w, h = img.size()知道;(如果之后转numpy数组会变成 [ H , W , C ] \color{red}{[H, W, C]} [H,W,C])
- 之后转Tensor变为
[
C
,
H
,
W
]
\color{red}{[C, H, W]}
[C,H,W],像素值由0-255变为0-1
修改dataset_val将没有标准化的、resize过的Tensor query图像取出:
输出mask图: - 在每一个打包后的dataloader中(这里是64张图片),将pred_mask移动到cpu上(不移动会报错),(张量与数组运算报错(Use Tensor.cpu() to copy the tensor to host memory first;RuntimeError: Expected all tensors to be on the same device))
- 转numpy数组后维度变为 [ C , H , W ] \color{red}{[C, H, W]} [C,H,W]
- 最后通过修改dataset_val得到query_name[i],img*255之后,通过cv2.imwrite保存图片(实验室服务器cv2.show函数会出问题)
- 不用加img_rgb = np.uint8(img_rgb),因为cv2.imwrite函数会自动改变数据类型。
for i in range(pred_label.shape[0]):
pred_mask = pred_label[i]
img = pred_mask.cpu().numpy()
cv2.imwrite(pth_file + '{}_pre.jpg'.format(query_name[i]), 255 * img)
cv2.waitKey(100)
5.3 输出对应于mask的原图(所预测的等比例resize后的原图) transpose和reshape的区别:在单色图中, intensity 是 强度 gray scale 是灰度。
而强度一般由 光源的能量和物体反射能量的比例的乘积 决定。
所以如果能量很低,颜色就很暗,极限就是能量为0,是黑色,而能量很大,就很亮,就是白色。
transpose 与 reshape 的最大区别: reshape 修改的只是维度,填充顺序不变,transpose 修改的是轴,填充顺序改变
- img_rgb输出后维度(3, 321, 321),由于是Image.open打开的,所以第一个维度的3表示每张321*321图的RGB值
- transpose((1, 2, 0))之后,一张321*321的矩阵,每个点都有RGB3个值,是正常的
- !!!如果使用reshape,就会出现问题,示例图如下:
img_rgb = img_rgb.cpu().numpy().transpose((1, 2, 0))[:, :, ::-1]
img_rgb = img_rgb.cpu().numpy().reshape([321, 321, 3])[:, :, ::-1]
原图:(没有resize为321, 321)resize之后应该为(3, 321, 321)
当使用reshape的时候,是类似于这样的,会造成困扰,所以怀疑是reshape函数不行:
不修改C通道:(RGB的使用cv2默认是BGR,红色的原图R被输出成了蓝色的B)
- RGB—>
- BGR
使用transpose后,再通过
[
:
,
:
,
:
:
−
1
]
\color{red}[:, :, ::-1]{}
[:,:,::−1]修改RGB为BGR,就完全正常了:(参考:pytorch实现HWC转CHW)
Ps:
i
m
g
2
=
i
m
g
[
:
,
:
,
[
2
,
1
,
0
]
]
\color{red}{img_2 = img[:,:,[2,1,0]]}
img2=img[:,:,[2,1,0]]将最后一个维度C—>BGR(0,1,2)转为RGB(2,1,0)
img_2 = img[:,:,[2,1,0]]
plt.imshow(img_2)
# c h w
img_rgb = query_img[i]
img_rgb = img_rgb.cpu().numpy().transpose((1, 2, 0))[:, :, ::-1]
# img_rgb = img_rgb.cpu().numpy().reshape([321, 321, 3])[:, :, ::-1]
# img_rgb = np.uint8(img_rgb)
cv2.imwrite(pth_file + '{}.jpg'.format(query_name[i]), img_rgb * 255)
cv2.waitKey(100)
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)