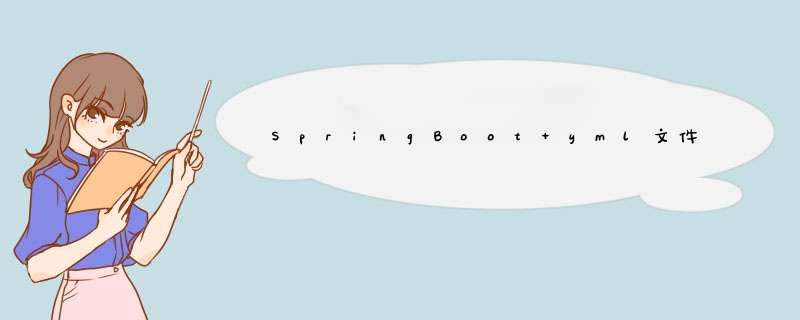
使用 @Value("表达式") 注解可以从配合文件中读取数据,注解中用于读取属性名引用方式是:${一级属性名.二级属性名……}
我们可以在 BookController 中使用 @Value 注解读取配合文件数据,如下
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
@Value("${lesson}")
private String lesson;
@Value("${server.port}")
private Integer port;
@Value("${enterprise.subject[0]}")
private String subject_00;
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public String getById(@PathVariable Integer id){
System.out.println(lesson);
System.out.println(port);
System.out.println(subject_00);
return "hello , spring boot!";
}
}
上面方式读取到的数据特别零散,SpringBoot 还可以使用 @Autowired 注解注入 Environment 对象的方式读取数据。这种方式 SpringBoot 会将配置文件中所有的数据封装到 Environment 对象中,如果需要使用哪个数据只需要通过调用 Environment 对象的 getProperty(String name) 方法获取。具体代码如下:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
@Autowired
private Environment env;
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public String getById(@PathVariable Integer id){
System.out.println(env.getProperty("lesson"));
System.out.println(env.getProperty("enterprise.name"));
System.out.println(env.getProperty("enterprise.subject[0]"));
return "hello , spring boot!";
}
}
自定义对象注意:这种方式,框架内容大量数据,而在开发中我们很少使用。
SpringBoot 还提供了将配置文件中的数据封装到我们自定义的实体类对象中的方式。具体 *** 作如下:
-
将实体类
bean的创建交给Spring管理。在类上添加
@Component注解 -
使用
@ConfigurationProperties注解表示加载配置文件在该注解中也可以使用
prefix属性指定只加载指定前缀的数据 -
在
BookController中进行注入
具体代码如下:
Enterprise 实体类内容如下:
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "enterprise")
public class Enterprise {
private String name;
private int age;
private String tel;
private String[] subject;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getTel() {
return tel;
}
public void setTel(String tel) {
this.tel = tel;
}
public String[] getSubject() {
return subject;
}
public void setSubject(String[] subject) {
this.subject = subject;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Enterprise{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", tel='" + tel + '\'' +
", subject=" + Arrays.toString(subject) +
'}';
}
}
BookController 内容如下:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
@Autowired
private Enterprise enterprise;
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public String getById(@PathVariable Integer id){
System.out.println(enterprise.getName());
System.out.println(enterprise.getAge());
System.out.println(enterprise.getSubject());
System.out.println(enterprise.getTel());
System.out.println(enterprise.getSubject()[0]);
return "hello , spring boot!";
}
}
注意:
使用第三种方式,在实体类上有如下警告提示
这个警告提示解决是在 pom.xml 中添加如下依赖即可
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processorartifactId>
<optional>trueoptional>
dependency>
springboot 配置文件分级
SpringBoot 中4级配置文件放置位置:
- 1级:classpath:application.yml 【最低】
- 2级:classpath:config/application.yml
- 3级:file :application.yml
- 4级:file :config/application.yml 【最高】
在jar包位置下的application.yml
config优先级最高
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)