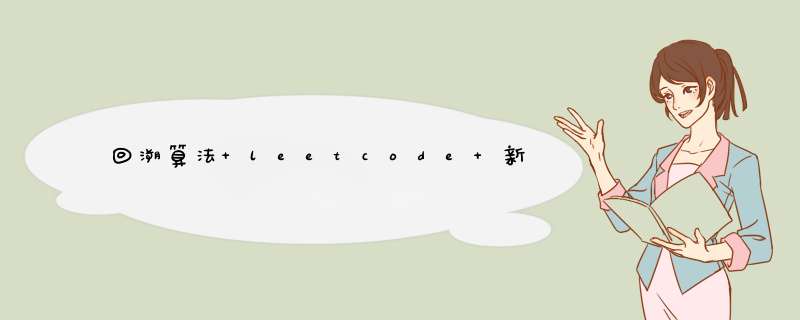
回溯法抽象为树形结构后,其遍历过程就是:「for循环横向遍历,递归纵向遍历,回溯不断调整结果集」。
回溯算法一般的代码形式:
def backtrack(参数):
if 终止条件:
更新结果集
return
for (选择本层集合中的元素):
处理节点
backtrack(路径,选择列表) //递归
77. 组合
class Solution(object):
def combine(self, n, k):
"""
:type n: int
:type k: int
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
if k > n:
return []
res = []
# path = []
def backtrack(startindex, n, k, path):
if len(path) == k: #终止条件
res.append(path) #存放结果
return
for i in range(startindex, n + 1): #startindex是确认起始的位置,之前用过的数不会参与到下一步的遍历中
backtrack(i + 1, n, k, path + [i])
return
backtrack(1, n, k, [])
return res
216. 组合总和 III
class Solution(object):
def combinationSum3(self, k, n):
"""
:type k: int
:type n: int
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
res = []
def backtrack(startindex, n, k, path):
if len(path) == k:
if sum(path) != n:
return
else:
res.append(path)
return
if sum(path) > n:
return
for i in range(startindex, 10):
backtrack(i + 1, n, k, path + [i])
return
backtrack(1, n, k, [])
return res
17. 电话号码的字母组合
我竟然参考着卡尔的自己写出来了。。。但是效率很低。
class Solution(object):
def letterCombinations(self, digits):
"""
:type digits: str
:rtype: List[str]
"""
phone = {
'2': ['a', 'b', 'c'],
'3': ['d', 'e', 'f'],
'4': ['g', 'h', 'i'],
'5': ['j', 'k', 'l'],
'6': ['m', 'n', 'o'],
'7': ['p', 'q', 'r', 's'],
'8': ['t', 'u', 'v'],
'9': ['w', 'x', 'y', 'z']}
def backtrack(index, combination):
if len(combination) == len(digits):
res.append(combination)
return
digit = digits[index]
letters = phone[digit]
for i in range(len(letters)):
backtrack(index+1, combination + letters[i])
return
res = []
if not digits:
return []
backtrack(0, "")
return res
class Solution(object):
def letterCombinations(self, digits):
"""
:type digits: str
:rtype: List[str]
"""
phone = {
'2': ['a', 'b', 'c'],
'3': ['d', 'e', 'f'],
'4': ['g', 'h', 'i'],
'5': ['j', 'k', 'l'],
'6': ['m', 'n', 'o'],
'7': ['p', 'q', 'r', 's'],
'8': ['t', 'u', 'v'],
'9': ['w', 'x', 'y', 'z']
}
def backtrack(combination, nextdigits):
if len(nextdigits) == 0:
res.append(combination)
return
for letter in phone[nextdigits[0]]:
backtrack(combination + letter, nextdigits[1:])
res = []
if not digits:
return []
backtrack('', digits)
return res
39. 组合总和 (自己严格按照回溯格式写出来的,但是效率很低)
class Solution(object):
def combinationSum(self, candidates, target):
"""
:type candidates: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
candidates.sort()
res = []
def backtrack(startindex, target, path):
if sum(path) == target:
res.append(path)
return
elif sum(path) > target:
return
for i in range(startindex, len(candidates)):
backtrack(i, target, path+[candidates[i]])
return
backtrack(0, target, [])
return res
40. 组合总和 II (continue的条件不理解,为什么会i-1>startindex???)
class Solution(object):
def combinationSum2(self, candidates, target):
"""
:type candidates: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
candidates.sort()
res = []
def backtrack(startindex, target, path):
if sum(path) == target:
res.append(path)
elif sum(path) > target:
return
for i in range(startindex, len(candidates)):
if candidates[i-1] == candidates[i] and i-1 >= startindex:
continue
backtrack(i+1, target, path+[candidates[i]])
return
backtrack(0, target, [])
return res
131. 分割回文串
class Solution(object):
def partition(self, s):
"""
:type s: str
:rtype: List[List[str]]
"""
length = len(s)
res = []
def dfs(start, tmp):
if start >= length:
res.append(tmp)
return
for i in range(start, length):
substring = s[start:i + 1]
if substring == substring[::-1]: #子串是回文串
dfs(i + 1, tmp+[substring])
return
dfs(0, [])
return res
下面这个不理解,tmp[:] 和 pop,但是应该要理解这个过程。
class Solution(object):
def partition(self, s):
"""
:type s: str
:rtype: List[List[str]]
"""
length = len(s)
res = []
def dfs(start, tmp):
if start >= length:
res.append(tmp[:])
for i in range(start, length):
substring = s[start:i + 1]
if substring == substring[::-1]: #子串是回文串
tmp.append(substring)
dfs(i + 1, tmp)
tmp.pop()
dfs(0, [])
return res
93. 复原 IP 地址
LeetCode 93 Restore IP Addresses(Python详解及实现)_toplatona-CSDN博客
class Solution(object):
def restoreIpAddresses(self, s):
"""
:type s: str
:rtype: List[str]
"""
def dfs(s, segment, res, ip):
if segment == 4:
if s == '':
res.append(ip[1:])
return
for i in range(1,4):
if i <= len(s):
if int(s[:i]) <= 255:
dfs(s[i:], segment+1, res, ip+'.'+s[:i])
if s[0] == '0':
break
res = []
dfs(s, 0, res, '')#segment 初始化为0
return res
78. 子集
class Solution(object):
def subsets(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
res = []
def temp(start, num):
res.append(num)
for i in range(start, len(nums)):
temp(i+1, num+[nums[i]])
temp(0, [])
return res
90. 子集 II
class Solution(object):
def subsetsWithDup(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
nums.sort() # sort the nums to find the equivalent nums
res = []
def temp(start, num):
res.append(num)
for i in range(start, len(nums)):
if i>start and nums[i] == nums[i-1]:
continue # pass the same number
else:
temp(i+1, num+[nums[i]])
temp(0, [])
return res
491. 递增子序列 (巨巨巨巨巨慢,只能先把所有的放入结果集然后再去重,要优化)
class Solution(object):
def findSubsequences(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
res = []
def backtrack(nums, startindex, path):
if len(path) >= 2 and path not in res:
res.append(path)
for i in range(startindex, len(nums)):
if not path or nums[i] >= path[-1] :
backtrack(nums, i+1, path+[nums[i]])
backtrack(nums, 0, [])
return res
46. 全排列
自己写的,因为是全排列所以要选取数组里的所有元素,不需要startindex。
class Solution(object):
def permute(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
res = []
def backtrack(path):
if len(path) == len(nums):
res.append(path)
return
for i in range(len(nums)):
if nums[i] not in path:
backtrack(path+[nums[i]])
return
backtrack([])
return res
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)