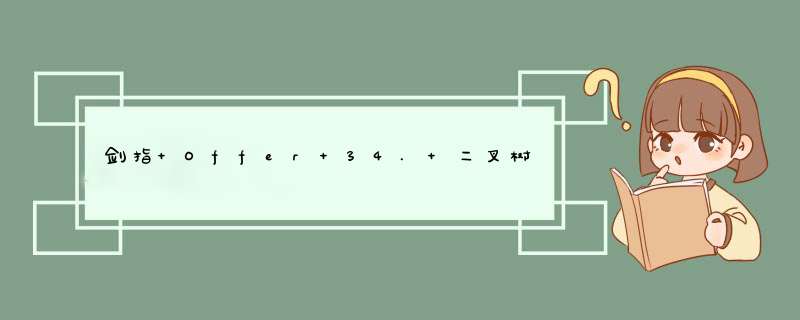
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个整数目标和 targetSum ,找出所有 从根节点到叶子节点 路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
输入:root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1], targetSum = 22
输出:[[5,4,11,2],[5,8,4,5]]
提示:
树中节点总数在范围 [0, 5000] 内
-1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
-1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
class Solution {
linkedList> result = new linkedList<>();
linkedList path = new linkedList<>();
public List> pathSum(TreeNode root, int target) {
backtrack(root, target);
return result;
}
void backtrack(TreeNode node, int target) {
if(node == null) {
return;
}
path.add(node.val);
if(node.left == null && node.right == null) {
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < path.size(); i++) {
sum = sum + path.get(i);
}
if(sum == target)result.add(new linkedList(path));
//值得注意的是,记录路径时若直接执行 result.add(path)象加入了 res ;后续 path 改变时, res 中的 path 对象也会随之改变。
//正确做法:result.add(new linkedList(path)),相当于复制了一个 path 并加入到 res。
}
// target = target - node.val;
// if(target == 0 && node.left == null && node.right == null)result.add(new linkedList(path));
backtrack(node.left, target);
backtrack(node.right, target);
//回溯的关键
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)