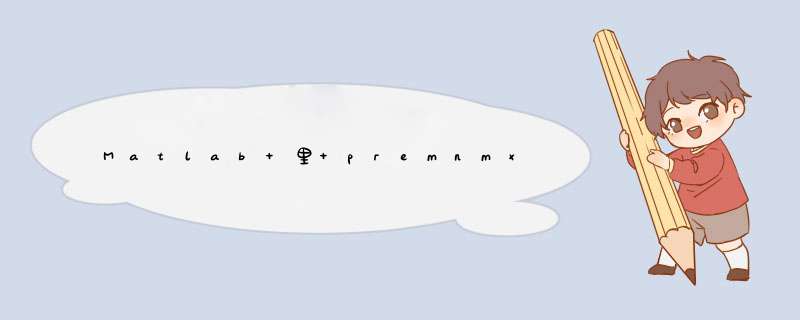
premnmx函数:用于将网络的输入数据或输出数据进行归一化,归一化后的数据将分布在[-1,1]区间内。tramnmx:使用网络时所用的新数据和样本数据接受相同的预处理函数。
postmnmx:常用的函数,网络输出结果需要进行反归一化还原成原始的数据。postmnmx语句的语法格式是:[PN] = postmnmx(P,minp,maxp)。
MATLAB包括拥有数百个内部函数的主包和三十几种工具包。工具包又可以分为功能性工具包和学科工具包。功能工具包用来扩充MATLAB的符号计算,可视化建模仿真,文字处理及实时控制等功能。学科工具包是专业性比较强的工具包,控制工具包,信号处理工具包,通信工具包等都属于此类。
扩展资料:
MATLAB应用程序接口(API)是一个使MATLAB语言能与C、Fortran等其它高级编程语言进行交互的函数库。
该函数库的函数通过调用动态链接库(DLL)实现与MATLAB文件的数据交换,其主要功能包括在MATLAB中调用C和Fortran程序,以及在MATLAB与其它应用程序间建立客户、服务器关系。
MATLAB实用源代码
1图像的读取及旋转
A=imread('');%读取图像
subplot(2,2,1),imshow(A),title('原始图像');%输出图像
I=rgb2gray(A);
subplot(2,2,2),imshow(A),title('灰度图像');
subplot(2,2,3),imhist(I),title('灰度图像直方图');%输出原图直方图
theta = 30;J = imrotate(I,theta);% Try varying the angle, theta
subplot(2,2,4), imshow(J),title(‘旋转图像’)
2边缘检测
I=imread('C:\Users\HP\Desktop\平时总结\路飞jpg');
subplot(2,2,1),imshow(I),title('原始图像');
I1=edge(I,'sobel');
subplot(2,2,2),imshow(I1),title('sobel边缘检测');
I2=edge(I,'prewitt');
subplot(2,2,3),imshow(I2),title('prewitt边缘检测');
I3=edge(I,'log');
subplot(2,2,4),imshow(I3),title('log边缘检测');
3图像反转
MATLAB 程序实现如下:
I=imread('xianbmp');
J=double(I);
J=-J+(256-1);%图像反转线性变换
H=uint8(J);
subplot(1,2,1),imshow(I);
subplot(1,2,2),imshow(H);
4灰度线性变换
MATLAB 程序实现如下:
I=imread('xianbmp');
subplot(2,2,1),imshow(I);
title('原始图像');
axis([50,250,50,200]);
axis on;%显示坐标系
I1=rgb2gray(I);
subplot(2,2,2),imshow(I1);
title('灰度图像');
axis([50,250,50,200]);
axis on; %显示坐标系
J=imadjust(I1,[01 05],[]); %局部拉伸,把[01 05]内的灰度拉伸为[0 1]
subplot(2,2,3),imshow(J);
title('线性变换图像[01 05]');
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %显示网格线
axis on; %显示坐标系
K=imadjust(I1,[03 07],[]); %局部拉伸,把[03 07]内的灰度拉伸为[0 1]
subplot(2,2,4),imshow(K);
title('线性变换图像[03 07]');
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %显示网格线
axis on; %显示坐标系
5非线性变换
MATLAB 程序实现如下:
I=imread('xianbmp');
I1=rgb2gray(I);
subplot(1,2,1),imshow(I1);
title(' 灰度图像');
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on;%显示网格线
axis on;%显示坐标系
J=double(I1);
J=40(log(J+1));
H=uint8(J);
subplot(1,2,2),imshow(H);
title(' 对数变换图像');
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %显示网格线
axis on; %显示坐标系
4直方图均衡化
MATLAB 程序实现如下:
I=imread('xianbmp');
I=rgb2gray(I);
figure;
subplot(2,2,1);
imshow(I);
subplot(2,2,2);
imhist(I);
I1=histeq(I);
figure;
subplot(2,2,1);
imshow(I1);
subplot(2,2,2);
imhist(I1);
5 线性平滑滤波器
用MATLAB实现领域平均法抑制噪声程序:
I=imread('xianbmp');
subplot(231)
imshow(I)
title('原始图像')
I=rgb2gray(I);
I1=imnoise(I,'salt & pepper',002);
subplot(232)
imshow(I1)
title(' 添加椒盐噪声的图像')
k1=filter2(fspecial('average',3),I1)/255; %进行33模板平滑滤波
k2=filter2(fspecial('average',5),I1)/255; %进行55模板平滑滤波k3=filter2(fspecial('average',7),I1)/255; %进行77模板平滑滤波
k4=filter2(fspecial('average',9),I1)/255; %进行99模板平滑滤波
subplot(233),imshow(k1);title('33 模板平滑滤波');
subplot(234),imshow(k2);title('55 模板平滑滤波');
subplot(235),imshow(k3);title('77 模板平滑滤波');
subplot(236),imshow(k4);title('99 模板平滑滤波');
6中值滤波器
用MATLAB实现中值滤波程序如下:
I=imread('xianbmp');
I=rgb2gray(I);
J=imnoise(I,'salt&pepper',002);
subplot(231),imshow(I);title('原图像');
subplot(232),imshow(J);title('添加椒盐噪声图像');
k1=medfilt2(J); %进行33模板中值滤波
k2=medfilt2(J,[5,5]); %进行55模板中值滤波
k3=medfilt2(J,[7,7]); %进行77模板中值滤波
k4=medfilt2(J,[9,9]); %进行99模板中值滤波
subplot(233),imshow(k1);title('33模板中值滤波');
subplot(234),imshow(k2);title('55模板中值滤波 ');
subplot(235),imshow(k3);title('77模板中值滤波');
subplot(236),imshow(k4);title('99 模板中值滤波');
7用Sobel算子和拉普拉斯对图像锐化:
I=imread('xianbmp');
subplot(2,2,1),imshow(I);
title('原始图像');
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %显示网格线
axis on;%显示坐标系
I1=im2bw(I);
subplot(2,2,2),imshow(I1);
title('二值图像');
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on;%显示网格线
axis on;%显示坐标系
H=fspecial('sobel');%选择sobel算子
J=filter2(H,I1); %卷积运算
subplot(2,2,3),imshow(J);
title('sobel算子锐化图像');
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %显示网格线
axis on;%显示坐标系
h=[0 1 0,1 -4 1,0 1 0]; %拉普拉斯算子
J1=conv2(I1,h,'same');%卷积运算
subplot(2,2,4),imshow(J1);
title('拉普拉斯算子锐化图像');
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %显示网格线
axis on; %显示坐标系
8梯度算子检测边缘
用 MATLAB实现如下:
I=imread('xianbmp');
subplot(2,3,1);
imshow(I);
title('原始图像');
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %显示网格线
axis on; %显示坐标系
I1=im2bw(I);
subplot(2,3,2);
imshow(I1);
title('二值图像');
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %显示网格线
axis on; %显示坐标系
I2=edge(I1,'roberts');
figure;
subplot(2,3,3);
imshow(I2);
title('roberts算子分割结果');
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %显示网格线
axis on; %显示坐标系
I3=edge(I1,'sobel');
subplot(2,3,4);
imshow(I3);
title('sobel算子分割结果');
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %显示网格线
axis on; %显示坐标系
I4=edge(I1,'Prewitt');
subplot(2,3,5);
imshow(I4);
title('Prewitt算子分割结果 ');
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %显示网格线
axis on; %显示坐标系
9LOG算子检测边缘
用 MATLAB程序实现如下:
I=imread('xianbmp');
subplot(2,2,1);
imshow(I);
title('原始图像');
I1=rgb2gray(I);
subplot(2,2,2);
imshow(I1);
title('灰度图像');
I2=edge(I1,'log');
subplot(2,2,3);
imshow(I2);
title('log算子分割结果');
10Canny算子检测边 缘
用MATLAB程序实现如下:
I=imread('xianbmp');
subplot(2,2,1);
imshow(I);
title('原始图像')
I1=rgb2gray(I);
subplot(2,2,2);
imshow(I1);
title('灰度图像');
I2=edge(I1,'canny');
subplot(2,2,3);
imshow(I2);
title('canny算子分割结果');
11边界跟踪 (bwtraceboundary函数)
clc
clear all
I=imread('xianbmp');
figure
imshow(I);
title('原始图像');
I1=rgb2gray(I); %将彩色图像转化灰度图像
threshold=graythresh(I1); %计算将灰度图像转化为二值图像所需的门限
BW=im2bw(I1, threshold); %将灰度图像转化为二值图像
figure
imshow(BW);
title('二值图像');
dim=size(BW);
col=round(dim(2)/2)-90; %计算起始点列坐标
row=find(BW(:,col),1); %计算起始点行坐标
connectivity=8;
num_points=180;
contour=bwtraceboundary(BW,[row,col],'N',connectivity,num_points);
%提取边界
figure
imshow(I1);
hold on;
plot(contour(:,2),contour(:,1), 'g','LineWidth' ,2);
title('边界跟踪图像');
12Hough变换
I= imread('xianbmp');
rotI=rgb2gray(I);
subplot(2,2,1);
imshow(rotI);
title('灰度图像');
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on;
axis on;
BW=edge(rotI,'prewitt');
subplot(2,2,2);
imshow(BW);
title('prewitt算子边缘检测 后图像');
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on;
axis on;
[H,T,R]=hough(BW);
subplot(2,2,3);
imshow(H,[],'XData',T,'YData',R,'InitialMagnification','fit');
title('霍夫变换图');
xlabel('\theta'),ylabel('\rho');
axis on , axis normal, hold on;
P=houghpeaks(H,5,'threshold',ceil(03max(H(:))));
x=T(P(:,2));y=R(P(:,1));
plot(x,y,'s','color','white');
lines=houghlines(BW,T,R,P,'FillGap',5,'MinLength',7);
subplot(2,2,4);,imshow(rotI);
title('霍夫变换图像检测');
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on;
axis on;
hold on;
max_len=0;
for k=1:length(lines)
xy=[lines(k)point1;lines(k)point2];
plot(xy(:,1),xy(:,2),'LineWidth',2,'Color','green');
plot(xy(1,1),xy(1,2),'x','LineWidth',2,'Color','yellow');
plot(xy(2,1),xy(2,2),'x','LineWidth',2,'Color','red');
len=norm(lines(k)point1-lines(k)point2);
if(len>max_len)
max_len=len;
xy_long=xy;
end
end
plot(xy_long(:,1),xy_long(:,2),'LineWidth',2,'Color','cyan');
13直方图阈值法
用 MATLAB实现直方图阈值法:
I=imread('xianbmp');
I1=rgb2gray(I);
figure;
subplot(2,2,1);
imshow(I1);
title(' 灰度图像')
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on;%显示网格线
axis on; %显示坐标系
[m,n]=size(I1);%测量图像尺寸参数
GP=zeros(1,256); %预创建存放灰度出现概率的向量
for k=0:255
GP(k+1)=length(find(I1==k))/(mn);%计算每级灰度出现的概率,将其存入GP中相应位置
end
subplot(2,2,2),bar(0:255,GP,'g')%绘制直方图
title('灰度直方图')
xlabel('灰度值')
ylabel(' 出现概率')
I2=im2bw(I,150/255);
subplot(2,2,3),imshow(I2);
title('阈值150的分割图像')
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %显示网格线
axis on; %显示坐标系
I3=im2bw(I,200/255); %
subplot(2,2,4),imshow(I3);
title('阈值200的分割图像')
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %显示网格线
axis on; %显示坐标系
14 自动阈值法:Otsu法
用MATLAB实现Otsu算法:
clc
clear all
I=imread('xianbmp');
subplot(1,2,1),imshow(I);
title('原始图像')
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %显示网格线
axis on; %显示坐标系
level=graythresh(I); %确定灰度阈值
BW=im2bw(I,level);
subplot(1,2,2),imshow(BW);
title('Otsu 法阈值分割图像')
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %显示网格线
axis on; %显示坐标系
15膨胀 *** 作
I=imread('xianbmp'); %载入图像
I1=rgb2gray(I);
subplot(1,2,1);
imshow(I1);
title('灰度图像')
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %显示网格线
axis on; %显示坐标系
se=strel('disk',1); %生成圆形结构元素
I2=imdilate(I1,se); %用生成的结构元素对图像进行膨胀
subplot(1,2,2);
imshow(I2);
title(' 膨胀后图像');
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %显示网格线
axis on; %显示坐标系
16腐蚀 *** 作
MATLAB 实现腐蚀 *** 作
I=imread('xianbmp'); %载入图像
I1=rgb2gray(I);
subplot(1,2,1);
imshow(I1);
title('灰度图像')
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %显示网格线
axis on; %显示坐标系
se=strel('disk',1); %生成圆形结构元素
I2=imerode(I1,se); %用生成的结构元素对图像进行腐蚀
subplot(1,2,2);
imshow(I2);
title('腐蚀后图像');
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on; %显示网格线
axis on; %显示坐标系
17开启和闭合 *** 作
用 MATLAB实现开启和闭合 *** 作
I=imread('xianbmp'); %载入图像
subplot(2,2,1),imshow(I);
title('原始图像');
axis([50,250,50,200]);
axis on; %显示坐标系
I1=rgb2gray(I);
subplot(2,2,2),imshow(I1);
title('灰度图像');
axis([50,250,50,200]);
axis on; %显示坐标系
se=strel('disk',1); %采用半径为1的圆作为结构元素
I2=imopen(I1,se); %开启 *** 作
I3=imclose(I1,se); %闭合 *** 作
subplot(2,2,3),imshow(I2);
title('开启运算后图像');
axis([50,250,50,200]);
axis on; %显示坐标系
subplot(2,2,4),imshow(I3);
title('闭合运算后图像');
axis([50,250,50,200]);
axis on; %显示坐标系
18开启和闭合组合 *** 作
I=imread('xianbmp');%载入图像
subplot(3,2,1),imshow(I);
title('原始图像');
axis([50,250,50,200]);
axis on;%显示坐标系
I1=rgb2gray(I);
subplot(3,2,2),imshow(I1);
title('灰度图像');
axis([50,250,50,200]);
axis on;%显示坐标系
se=strel('disk',1);
I2=imopen(I1,se);%开启 *** 作
I3=imclose(I1,se);%闭合 *** 作
subplot(3,2,3),imshow(I2);
title('开启运算后图像');
axis([50,250,50,200]);
axis on;%显示坐标系
subplot(3,2,4),imshow(I3);
title('闭合运算后图像');
axis([50,250,50,200]);
axis on;%显示坐标系
se=strel('disk',1);
I4=imopen(I1,se);
I5=imclose(I4,se);
subplot(3,2,5),imshow(I5);%开—闭运算图像
title('开—闭运算图像');
axis([50,250,50,200]);
axis on;%显示坐标系
I6=imclose(I1,se);
I7=imopen(I6,se);
subplot(3,2,6),imshow(I7);%闭—开运算图像
title('闭—开运算图像');
axis([50,250,50,200]);
axis on;%显示坐标系
19形态学边界提取
利用 MATLAB实现如下:
I=imread('xianbmp');%载入图像
subplot(1,3,1),imshow(I);
title('原始图像');
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on;%显示网格线
axis on;%显示坐标系
I1=im2bw(I);
subplot(1,3,2),imshow(I1);
title('二值化图像');
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on;%显示网格线
axis on;%显示坐标系
I2=bwperim(I1); %获取区域的周长
subplot(1,3,3),imshow(I2);
title('边界周长的二值图像');
axis([50,250,50,200]);
grid on;
axis on;
20形态学骨架提取
利用MATLAB实现如下:
I=imread('xianbmp');
subplot(2,2,1),imshow(I);
title('原始图像');
axis([50,250,50,200]);
axis on;
I1=im2bw(I);
subplot(2,2,2),imshow(I1);
title('二值图像');
axis([50,250,50,200]);
axis on;
I2=bwmorph(I1,'skel',1);
subplot(2,2,3),imshow(I2);
title('1次骨架提取');
axis([50,250,50,200]);
axis on;
I3=bwmorph(I1,'skel',2);
subplot(2,2,4),imshow(I3);
title('2次骨架提取');
axis([50,250,50,200]);
axis on;
21直接提取四个顶点坐标
I = imread('xianbmp');
I = I(:,:,1);
BW=im2bw(I);
figure
imshow(~BW)
[x,y]=getpts
平滑滤波
h=fspecial('average',9);
I_gray=imfilter(I_gray,h,'replicate');%平滑滤波
x=fsolve(fun,x0)求解fun(x)=0的解,x0是初值,fun是函数,x就是解 \r\n因为fsolve使用迭代法求解方程的,所以总要有个迭代的初值吧,这个初值就是你给的x0。 \r\n比如解方程组 \r\nx(1)^2+x(2)^2=1 \r\nx(1)=2x(2) \r\n可以写成 \r\nf=@(x)([x(1)^2+x(2)^2-1;x(1)-2x(2)]) \r\nx=fsolve(f,[1 1]) \r\n这里[1 1]就是初值,其实初值一般情况下可以随便给的。
function [y,y1]=select(ImageData,h,w)%取得最佳阈值将图像二值化
thr=05;delta=005;
y=(ImageData>=thrmean(max(ImageData)));
BW2=bwareaopen(y,10);%删除小面积对象
%格式:BW2 = bwareaopen(BW,P,conn)
%作用:删除二值图像BW中面积小于P的对象,默认情况下conn使用8邻域。
SE=strel('square',15);%创建一个正方形的结构元素
%SE = strel(shape, parameters)
%根据shape指定的类型创建一个结构元素SE。
IM2=imdilate(BW2,SE);%图像膨胀
IM3=imerode(IM2,SE);%图像腐蚀
%1开运算(先腐蚀后膨胀的过程):利用它可以消除小物体,在纤细点处分离物体,平滑较大物体边界,但同时并不明显改变原来物体的面积。OPEN(X,B)
%2闭运算(先膨胀后腐蚀的过程):利用它可以填充物体内细小空洞,连接临近物体、平滑其边界,但同时并不明显改变原来物体的面积。CLOSE(X,B)
average=sum(sum(IM3))/(hw); %将图像二值化
while(average<003||average>008)
if(average<003)
thr=thr-delta;
else
thr=thr+delta;
end
y=(ImageData>=thrmean(max(ImageData)));%求向量元素的平均值
BW2=bwareaopen(y,10);%再一次删除小面积
IM2=imdilate(BW2,SE);%膨胀
IM3=imerode(IM2,SE);%腐蚀
average=sum(sum(IM3))/(hw);%求灰度的平均值
end
y1=y;
y=IM3;
在Matlab中,cos函数可以使用cos(x)来表示,其中x是角度,而不是弧度。这是因为Matlab默认输入的是度数值,而不是弧度值。因此,如果需要计算cosx的值,可以直接在Matlab命令窗口中输入cos(x)即可。
需要注意的是,如果输入的是弧度值,则需要先将其转换为角度值并再进行计算。Matlab中,可以使用rad2deg函数将弧度转化为角度,也可以使用deg2rad函数将角度转化为弧度。
除了cos函数,Matlab还提供了许多数学函数,如sin、tan、log等等,都可以很方便地进行计算。同时,在Matlab中还可以进行向量和矩阵的计算,使得计算更加高效和灵活。
需要注意的是,Matlab中的cos函数是基于双精度浮点数的,因此在计算时可能存在精度误差。如果需要进行高精度计算,可以考虑使用符号计算工具箱或其他数值计算软件。
% rgb=imread('source1bmp');
% I=rgb2gray(rgb); % 色彩转换成灰度
I=imread('source3bmp');
level= graythresh(I); %得到合适的阈值 得到合适的阈值
bw= im2bw(I,level); %二值化
SE= strel('square',3); %设置膨胀结构元素
BW1= imdilate(bw,SE); % 膨胀
SE1= strel('arbitrary',eye(5)); %设置腐蚀结构元素
BW2= imerode(bw,SE1); %腐蚀
BW3= bwmorph(bw,'open'); %开运算
BW4= bwmorph(bw,'close'); %闭运算
figure(1),
subplot(2,3,1),imshow(I);title('原图');
subplot(2,3,2),imshow(bw);title('二值图');
subplot(2,3,3),imshow(BW1);title('膨胀');
subplot(2,3,4),imshow(BW2);title('腐蚀');
subplot(2,3,5),imshow(BW3);title('开运算');
subplot(2,3,6),imshow(BW4);title('闭运算');
%
figure(2)
BW5 = imfill(bw,'holes');
subplot(121), imshow(bw), title('源图像二值化')
subplot(122), imshow(BW5), title('填充后的图像')
%轮廓提取
figure(3)
contour = bwperim(bw);
imshow(contour);
title('轮廓')
步骤1,读取图像cameramantif (该图像是Matlab当前目录下自带的)
>> BW1=imread('cameramantif');
步骤2,创建一个任意形状的结构元素对象
>> SE=strel('arbitrary',eye(5));
步骤3,以图像BW1和结构元素SE为参数调用imerode函数进行腐蚀 *** 作。
>> BW2=imerode(BW1,SE);
步骤4,显示 *** 作结果
>> imshow(BW1)
>> figure,imshow(BW2)
图像cameramantif 腐蚀前后的效果对比!
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)