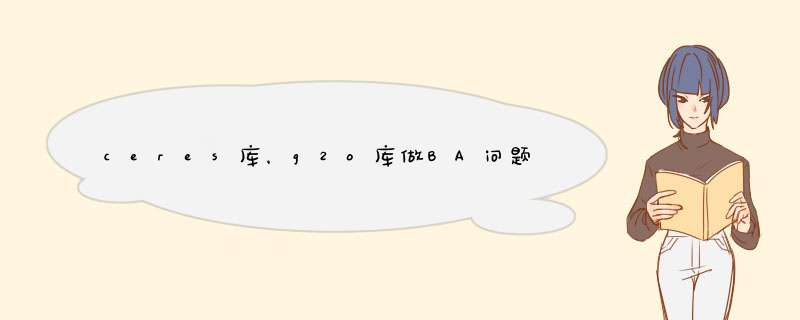
BA是Bundle Adjustment,Bundle指bundles of light rays。
也就是说,通过调整(adjustment) 各相机姿态和各特征点的空间位置,使这些光线最终收束到相机的光心。
相机坐标系到归一化坐标,畸变模型这些就不说了。
BA求解本质上是用最小二乘法优化一个误差,这个误差是观测点与实际的路标通过相机外参映射到像素坐标系的点的误差。
e
=
z
−
h
(
T
,
p
)
e = z - h(T, p)
e=z−h(T,p)
而需要调整的变量是相机位姿和路标(两个同时调整)。
以高斯牛顿法为例,还是要求雅可比矩阵J,然后H = JJT, b=-Je,
H
Δ
x
=
b
H\Delta x = b
HΔx=b,
求更新量
Δ
x
\Delta x
Δx, 不断迭代更新。
这里面临的问题是直接求H-1运算量随着特征点增加会非常大。
所以利用了H矩阵的稀疏性质,通过消元可以把路标点的那部分给整成对角矩阵。
理论依据就是消元后固定路标点的更新量,先求相机位姿的更新量,
求完了以后代回去,再求路标点的更新量。
当然这个更新,消元都可以用Ceres, g2o库来解决。
下面就是Ceres, g2o库求解BA的代码。
BA数据集用的是华盛顿大学给出的一个,参考链接
数据格式,相机坐标系到像素坐标系的转换方法也在链接中,它的只有归一化相机坐标,原点在光心,而不是以往的原点在左上角。
有畸变模型在里面。
Ceres实现主要注意的就是要重载()运算符,定义残差。
然后用ceres::Solve函数求解。
包含了下面的include的头文件,当然里面还有自带的其他头文件,就不写了,完整代码参考代码链接
#include 还有一个主函数
void SolveBA(BALProblem &bal_problem) {
const int point_block_size = bal_problem.point_block_size();
const int camera_block_size = bal_problem.camera_block_size();
double *points = bal_problem.mutable_points();
double *cameras = bal_problem.mutable_cameras();
// Observations is 2 * num_observations long array observations
// [u_1, u_2, ... u_n], where each u_i is two dimensional, the x
// and y position of the observation.
const double *observations = bal_problem.observations();
ceres::Problem problem;
for (int i = 0; i < bal_problem.num_observations(); ++i) {
ceres::CostFunction *cost_function;
// Each Residual block takes a point and a camera as input
// and outputs a 2 dimensional Residual
cost_function = SnavelyReprojectionError::Create(observations[2 * i + 0], observations[2 * i + 1]);
// If enabled use Huber's loss function.
ceres::LossFunction *loss_function = new ceres::HuberLoss(1.0);
// Each observation corresponds to a pair of a camera and a point
// which are identified by camera_index()[i] and point_index()[i]
// respectively.
double *camera = cameras + camera_block_size * bal_problem.camera_index()[i];
double *point = points + point_block_size * bal_problem.point_index()[i];
problem.AddResidualBlock(cost_function, loss_function, camera, point);
}
// show some information here ...
std::cout << "bal problem file loaded..." << std::endl;
std::cout << "bal problem have " << bal_problem.num_cameras() << " cameras and "
<< bal_problem.num_points() << " points. " << std::endl;
std::cout << "Forming " << bal_problem.num_observations() << " observations. " << std::endl;
std::cout << "Solving ceres BA ... " << endl;
ceres::Solver::Options options;
options.linear_solver_type = ceres::LinearSolverType::SPARSE_SCHUR;
options.minimizer_progress_to_stdout = true;
ceres::Solver::Summary summary;
ceres::Solve(options, &problem, &summary);
std::cout << summary.FullReport() << "\n";
}
(2)g2o库解BA
g2o是一个图优化库,主要需要注意的是添加顶点和边,第一个顶点要固定住。
g2o如果是自己定义顶点,要继承BaseVertex类,自己定义边的话继承BaseBinaryEdge类,
继承后要实现基类中的一些virtual函数,
主要有以下要覆盖的:
1.设置原点:setToOriginImpl()
2.读写函数,读入数据,写出数据,不需要的时候就直接返回一个boolean,
virtual bool read(istream &in), virtual bool write(ostream &out)
3.update时的更新函数:virtual void oplusImpl(const double *update)
4.计算误差函数,用在边继承里面:virtual void computeError()
g2o库还有几个函数解释一下:
setEstimate函数:
g2o库自带的有_estimate变量,通过setEstimate函数来设置这个_estimate, 当要读取更新后的_estimate时,
用顶点的estimate()函数。
setMeasurement也是一样的原理。
/// 位姿加相机内参的顶点,9维,前三维为so3,接下去为t, f, k1, k2
//继承BaseVertex类,<9,T>, 9表示图顶点的最小维度,g2o是图优化库, T表示内部使用的表示估计的类
class VertexPoseAndIntrinsics : public g2o::BaseVertex<9, PoseAndIntrinsics> {
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW; //new一个对象时会返回一个对齐的指针,指针内存位数对齐,因为Eigen为了加速使用了128位的指针,默认构造函数x86指针是32位
VertexPoseAndIntrinsics() {}
//加override, 强制在派生类中重写该函数,为了满足继承的所有条件,加override可以在派生类中写错时报错
//设置原点 *** 作
virtual void setToOriginImpl() override {
_estimate = PoseAndIntrinsics();
}
//实现相加运算符
virtual void oplusImpl(const double *update) override {
_estimate.rotation = SO3d::exp(Vector3d(update[0], update[1], update[2])) * _estimate.rotation; //更新rotation
_estimate.translation += Vector3d(update[3], update[4], update[5]);
_estimate.focal += update[6];
_estimate.k1 += update[7];
_estimate.k2 += update[8];
}
///根据估计值投影一个点
Vector2d project(const Vector3d &point) {
Vector3d pc = _estimate.rotation * point + _estimate.translation; //旋转+平移
//还是按https://grail.cs.washington.edu/projects/bal/的计算方法
pc = -pc / pc[2]; //归一化相机坐标
double r2 = pc.squaredNorm(); //长度的平方
double distortion = 1.0 + r2 * (_estimate.k1 + _estimate.k2 * r2);
return Vector2d(_estimate.focal * distortion * pc[0], _estimate.focal * distortion * pc[1]);
}
virtual bool read(istream &in) {return true;}
virtual bool write(ostream &out) const {return true;}
};
class VertexPoint : public g2o::BaseVertex<3, Eigen::Vector3d> {
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;
VertexPoint() {}
//设置原点 *** 作
virtual void setToOriginImpl() override {
_estimate = Vector3d(0, 0, 0);
}
//实现相加运算符
virtual void oplusImpl(const double *update) override{
_estimate += Vector3d(update[0], update[1], update[2]);
}
virtual bool read(istream &in) {return true;}
virtual bool write(ostream &out) const {return true;}
};
//图的边映射
//4个参数:2:测量值(x,y), Vector2d:测量值的类型, 后面两个是不同顶点的类型
class EdgeProjection : public g2o::BaseBinaryEdge<2, Vector2d, VertexPoseAndIntrinsics, VertexPoint> {
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;
virtual void computeError() override {
auto v0 = (VertexPoseAndIntrinsics *) _vertices[0]; //相机参数,位姿
auto v1 = (VertexPoint *) _vertices[1]; //观测点位置
auto proj = v0->project(v1->estimate()); //映射到像素坐标,后面计算像素上的误差
_error = proj - _measurement; //推测值和测量值的误差
}
virtual bool read(istream &in) {}
virtual bool write(ostream &out) const {}
};
void SolveBA(BALProblem &bal_problem) {
const int point_block_size = bal_problem.point_block_size();
const int camera_block_size = bal_problem.camera_block_size();
double *points = bal_problem.mutable_points();
double *cameras = bal_problem.mutable_cameras();
//位姿维度为9, 观测点为3维
typedef g2o::BlockSolver<g2o::BlockSolverTraits<9, 3>> BlockSolverType;
typedef g2o::LinearSolverCSparse<BlockSolverType::PoseMatrixType> LinearSolverType;
//use LM
auto solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg(
g2o::make_unique<BlockSolverType>(g2o::make_unique<LinearSolverType>()) //std::unique_ptr可以使用 make_uniqueunique_ptr 数组创建 ,但不能make_unique使用初始化数组元素
); //向 C unique_ptr ++ 标准库容器添加实例非常高效,因为移动 unique_ptr 构造函数无需复制 *** 作。
g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer;
optimizer.setAlgorithm(solver);
optimizer.setVerbose(true);
//build g2o problem
const double *observations = bal_problem.observations();
//vertex
vector<VertexPoseAndIntrinsics *> vertex_pose_intrinsics;
vector<VertexPoint *> vertex_points;
//存入每个相机的位姿内参
for(int i = 0; i < bal_problem.num_cameras(); ++i) {
VertexPoseAndIntrinsics *v = new VertexPoseAndIntrinsics();
double *camera = cameras + camera_block_size * i;
v->setId(i);
v->setEstimate(PoseAndIntrinsics(camera)); //_estimate = camera, update cache
optimizer.addVertex(v);
vertex_pose_intrinsics.push_back(v);
}
//存入观测点,3维
for(int i = 0; i < bal_problem.num_points(); ++i) {
VertexPoint *v = new VertexPoint();
double *point = points + point_block_size * i;
v->setId(i + bal_problem.num_cameras()); //data format中,camera存完了后面才是point
v->setEstimate(Vector3d(point[0], point[1], point[2])); //设置_estimate变量
//g2o需要在BA中手动设置待Marg的点
v->setMarginalized(true); //边缘概率估计的是xp
optimizer.addVertex(v);
vertex_points.push_back(v);
}
//edge
for(int i = 0; i < bal_problem.num_observations(); ++i) {
EdgeProjection *edge = new EdgeProjection;
edge->setVertex(0, vertex_pose_intrinsics[bal_problem.camera_index()[i]]);
edge->setVertex(1, vertex_points[bal_problem.point_index()[i]]);
edge->setMeasurement(Vector2d(observations[2 * i + 0], observations[2 * i + 1]));
edge->setInformation(Matrix2d::Identity()); //g2o内部的_information矩阵
edge->setRobustKernel(new g2o::RobustKernelHuber());
optimizer.addEdge(edge);
}
optimizer.initializeOptimization();
optimizer.optimize(40); //迭代次数
//set to bal problem//更新数据
for(int i = 0; i < bal_problem.num_cameras(); ++i) {
double *camera = cameras + camera_block_size * i;
auto vertex = vertex_pose_intrinsics[i];
auto estimate = vertex->estimate();
estimate.set_to(camera);
}
for(int i = 0; i < bal_problem.num_points(); i++) {
double *point = points + point_block_size * i;
auto vertex = vertex_points[i];
for(int k = 0; k < 3; k++) point[k] = vertex->estimate()[k];
}
}
ply文件的显示用meshlab
效果图:
没有优化之前的:
ceres优化之后的
g2o优化后的
看下初始状态和优化后的对比,可看到初始状态噪声比较大,而优化后较聚集
看下ceres和g2o的对比吧,都会收敛一些,但是位置会有一些错开
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)